Contents
Normalizers
Normalizers are used for converting raw events that come from various sources in different formats to the KUMA event data model. Normalized events become available for processing by other KUMA resources and services.
A normalizer consists of the main event parsing rule and optional additional event parsing rules. By creating a main parsing rule and a set of additional parsing rules, you can implement complex event processing logic. Data is passed along the tree of parsing rules depending on the conditions specified in the
Extra normalization conditions setting. The sequence in which parsing rules are created is significant: the event is processed sequentially and the processing sequence is indicated by arrows.
A normalizer is created in several steps:
- Preparing to create a normalizer
A normalizer can be created in the KUMA web interface:
- In the Resources → Normalizers section.
- When creating a collector, at the Event parsing step.
Then parsing rules must be created in the normalizer.
- Creating the main parsing rule for an event
The main parsing rule is created using the Add event parsing button. This opens the Event parsing window, where you can specify the settings of the main parsing rule:
- Specify event parsing settings.
- Specify event enrichment settings.
The main parsing rule for an event is displayed in the normalizer as a dark circle. You can view or modify the settings of the main parsing rule by clicking this circle. When you hover the mouse over the circle, a plus sign is displayed. Click it to add the parsing rules.
The name of the main parsing rule is used in KUMA as the normalizer name.
- Creating additional event parsing rules
Clicking the plus icon that is displayed when you hover the mouse over the circle or the block corresponding to the normalizer opens the Additional event parsing window where you can specify the settings of the additional parsing rule:
- Specify the conditions for sending data to the new normalizer.
- Specify event parsing settings.
- Specify event enrichment settings.
The additional event parsing rule is displayed in the normalizer as a dark block. The block displays the triggering conditions for the additional parsing rule, the name of the additional parsing rule, and the event field. When this event field is available, the data is passed to the normalizer. Click the block of the additional parsing rule to view or modify its settings.
If you hover the mouse over the additional normalizer, a plus button appears. You can use this button to create a new additional event parsing rule. To delete a normalizer, use the button with the trash icon.
- Completing the creation of the normalizer
To finish the creation of the normalizer, click Save.
In the upper right corner, in the search field, you can search for additional parsing rules by name.
For normalizer resources, you can enable the display of control characters in all input fields except the Description field.
If, when changing the settings of a collector resource set, you change or delete conversions in a normalizer connected to it, the edits will not be saved, and the normalizer itself may be corrupted. If you need to modify conversions in a normalizer that is already part of a service, the changes must be made directly to the normalizer under Resources → Normalizers in the web interface.
Event parsing settings
You can configure the rules for converting incoming events to the KUMA format when creating event parsing rules in the normalizer settings window, on the Normalization scheme tab.
Available settings:
- Name (required)—name of the parsing rules. Must contain 1 to 128 Unicode characters. The name of the main parsing rule is used as the name of the normalizer.
- Tenant (required)—name of the tenant that owns the resource.
This setting is not available for extra parsing rules.
- Parsing method (required)—drop-down list for selecting the type of incoming events. Depending on your choice, you can use the preconfigured rules for matching event fields or set your own rules. When you select some parsing methods, additional parameter fields required for filling in may become available.
Available parsing methods:
- Keep raw event (required)—in this drop-down list, indicate whether you need to store the raw event in the newly created normalized event. Available values:
- Don't save—do not save the raw event. This is the default setting.
- Only errors—save the raw event in the
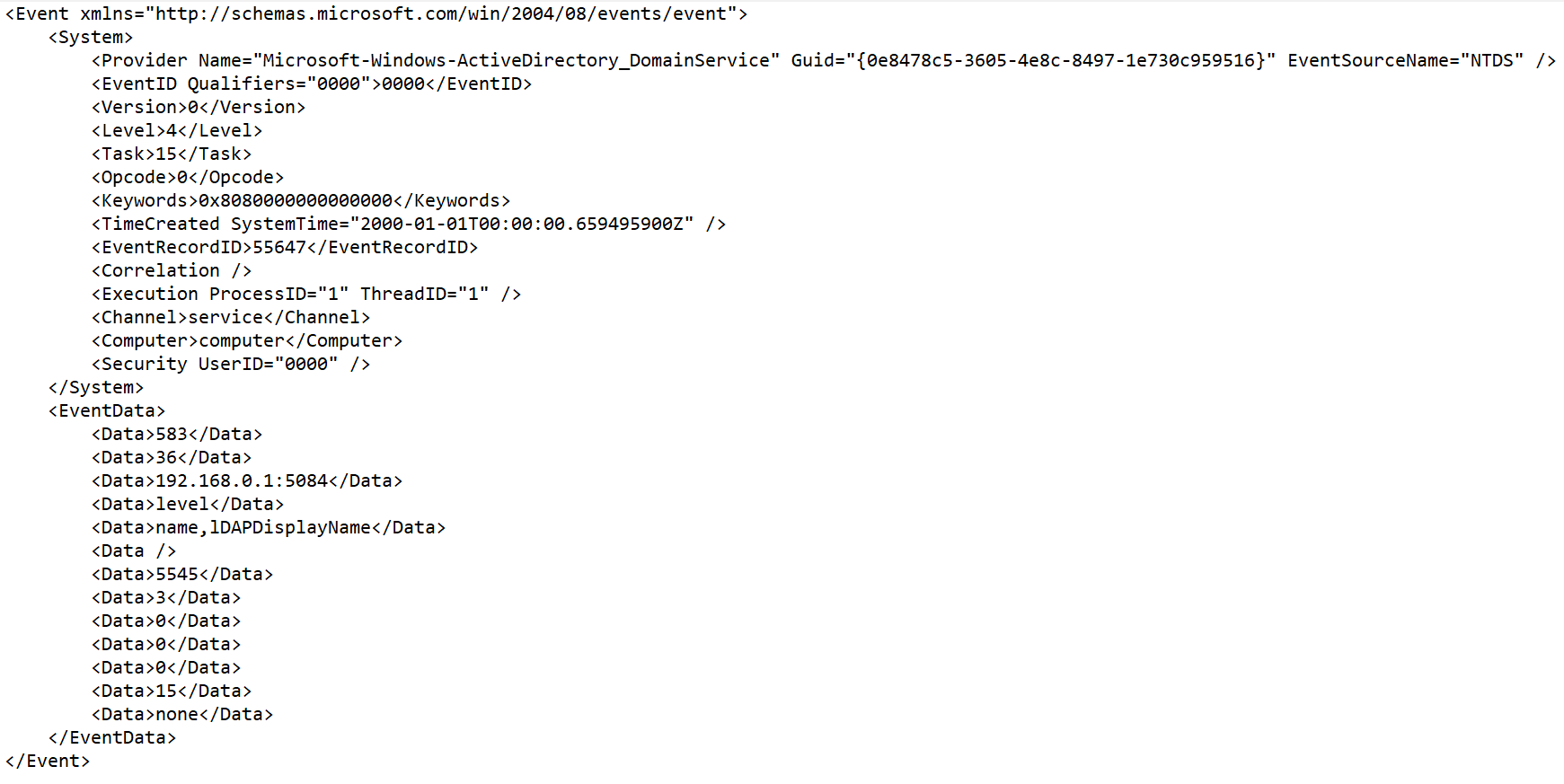
Rawfield of the normalized event if errors occurred when parsing it. This value is convenient to use when debugging a service. In this case, every time an event has a non-emptyRawfield, you know there was a problem.If fields containing the names
*Addressor*Date*do not comply with normalization rules, these fields are ignored. No normalization error occurs in this case, and the values of the fields are not displayed in theRawfield of the normalized event even if the Keep raw event → Only errors option was selected. - Always—always save the raw event in the
Rawfield of the normalized event.
This setting is not available for extra parsing rules.
- Keep extra fields (required)—in this drop-down list, you can choose whether you want to save fields and their values if no mapping rules have been configured for them (see below). This data is saved as an array in the
Extraevent field. Normalized events can be searched and filtered based on the data stored in theExtrafield.Filtering based on data from the Extra event field
By default, no extra fields are saved.
- Description—resource description: up to 4,000 Unicode characters.
This setting is not available for extra parsing rules.
- Event examples—in this field, you can provide an example of data that you want to process.
This setting is not available for the following parsing methods: netflow5, netflow9, sflow5, ipfix, sql.
The Event examples field is populated with data obtained from the raw event if the event was successfully parsed and the type of data obtained from the raw event matches the type of the KUMA field.
For example, the value "192.168.0.1" enclosed in quotation marks is not displayed in the SourceAddress field, in this case the value 192.168.0.1 is displayed in the Event examples field.
- Mapping settings block—here you can configure mapping of raw event fields to fields of the event in KUMA format:
- Source—column for the names of the raw event fields that you want to convert into KUMA event fields.
Clicking the
 button next to the field names in the Source column opens the Conversion window, in which you can use the Add conversion button to create rules for modifying the original data before they are written to the KUMA event fields. In the Conversion window, you can swap the added rules by dragging them by the
button next to the field names in the Source column opens the Conversion window, in which you can use the Add conversion button to create rules for modifying the original data before they are written to the KUMA event fields. In the Conversion window, you can swap the added rules by dragging them by the  icon; you can also delete them using the
icon; you can also delete them using the  icon.
icon. - KUMA field—drop-down list for selecting the required fields of KUMA events. You can search for fields by entering their names in the field.
- Label—in this column, you can add a unique custom label to event fields that begin with
DeviceCustom*andFlex*.
New table rows can be added by using the Add row button. Rows can be deleted individually using the
 button or all at once using the Clear all button.
button or all at once using the Clear all button.If you have loaded data into the Event examples field, the table will have an Examples column containing examples of values carried over from the raw event field to the KUMA event field.
If the size of the KUMA event field is less than the length of the value placed in it, the value is truncated to the size of the event field.
- Source—column for the names of the raw event fields that you want to convert into KUMA event fields.
Enrichment in the normalizer
When creating event parsing rules in the normalizer settings window, on the Enrichment tab, you can configure the rules for adding extra data to the fields of the normalized event using enrichment rules. These enrichment rules are stored in the settings of the normalizer where they were created.
Enrichments are created by using the Add enrichment button. There can be more than one enrichment rule. You can delete enrichment rules by using the  button.
button.
Settings available in the enrichment rule settings block:
- Source kind (required)—drop-down list for selecting the type of enrichment. Depending on the selected type, you may see advanced settings that will also need to be completed.
Available Enrichment rule source types:
- Target field (required)—drop-down list for selecting the KUMA event field that should receive the data.
This setting is not available for the enrichment source of the Table type.
Conditions for forwarding data to an extra normalizer
When creating additional event parsing rules, you can specify the conditions. When these conditions are met, the events are sent to the created parsing rule for processing. Conditions can be specified in the Additional event parsing window, on the Extra normalization conditions tab. This tab is not available for the basic parsing rules.
Available settings:
- Field to pass into normalizer—indicates the event field if you want only events with fields configured in normalizer settings to be sent for additional parsing.
If this field is blank, the full event is sent to the extra normalizer for processing.
- Set of filters—used to define complex conditions that must be met by the events received by the normalizer.
You can use the Add condition button to add a string containing fields for identifying the condition (see below).
You can use the Add group button to add a group of filters. Group operators can be switched between AND, OR, and NOT. You can add other condition groups and individual conditions to filter groups.
You can swap conditions and condition groups by dragging them by the
 icon; you can also delete them using the
icon; you can also delete them using the  icon.
icon.
Filter condition settings:
- Left operand and Right operand—used to specify the values to be processed by the operator.
In the left operand, you must specify the original field of events coming into the normalizer. For example, if the eventType - DeviceEventClass mapping is configured in the Basic event parsing window, then in the Additional event parsing window on the Extra normalization conditions tab, you must specify eventType in the left operand field of the filter. Data is processed only as text strings.
- Operators:
- = – full match of the left and right operands.
- startsWith – the left operand starts with the characters specified in the right operand.
- endsWith – the left operand ends with the characters specified in the right operand.
- match – the left operand matches the regular expression (RE2) specified in the right operand.
- in – the left operand matches one of the values specified in the right operand.
The incoming data can be converted by clicking the  button. The Conversion window opens, where you can use the Add conversion button to create the rules for converting the source data before any actions are performed on them. In the Conversion window, you can swap the added rules by dragging them by the
button. The Conversion window opens, where you can use the Add conversion button to create the rules for converting the source data before any actions are performed on them. In the Conversion window, you can swap the added rules by dragging them by the ![]() icon; you can also delete them using the
icon; you can also delete them using the  icon.
icon.
Supported event sources
KUMA supports the normalization of events coming from systems listed in the "Supported event sources" table. Normalizers for these systems are included in the distribution kit.
Supported event sources
System name |
Normalizer name |
Type |
Normalizer description |
|---|---|---|---|
1C EventJournal |
[OOTB] 1C EventJournal Normalizer |
xml |
Designed for processing the event log of the 1C system. The event source is the 1C log. |
1C TechJournal |
[OOTB] 1C TechJournal Normalizer |
regexp |
Designed for processing the technology event log. The event source is the 1C technology log. |
Absolute Data and Device Security (DDS) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
AhnLab Malware Defense System (MDS) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Ahnlab UTM |
[OOTB] Ahnlab UTM |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Ahnlab system. The event sources is system logs, operation logs, connections, the IPS module. |
AhnLabs MDS |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Apache Cassandra |
[OOTB] Apache Cassandra file |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the logs of the Apache Cassandra database version 4.0. |
Aruba ClearPass |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Avigilon Access Control Manager (ACM) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Ayehu eyeShare |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Barracuda Networks NG Firewall |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
BeyondTrust Privilege Management Console |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
BeyondTrust’s BeyondInsight |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Bifit Mitigator |
[OOTB] Bifit Mitigator Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the DDOS Mitigator protection system received via Syslog. |
Bloombase StoreSafe |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
BMC CorreLog |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Bricata ProAccel |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Brinqa Risk Analytics |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Broadcom Symantec Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Broadcom Symantec Endpoint Protection |
[OOTB] Broadcom Symantec Endpoint Protection |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Symantec Endpoint Protection system. |
Broadcom Symantec Endpoint Protection Mobile |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Broadcom Symantec Threat Hunting Center |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Canonical LXD |
[OOTB] Canonical LXD syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received via syslog from the Canonical LXD system version 5.18. |
Checkpoint |
[OOTB] Checkpoint Syslog CEF by CheckPoint |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from the Checkpoint event source via the Syslog protocol in the CEF format. |
Cisco Access Control Server (ACS) |
[OOTB] Cisco ACS syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Cisco Access Control Server (ACS) system received via Syslog. |
Cisco ASA |
[OOTB] Cisco ASA Extended v 0.1 |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Cisco ASA devices. Cisco ASA base extended set of events. |
Cisco Email Security Appliance (WSA) |
[OOTB] Cisco WSA AccessFile |
regexp |
Designed for processing the event log of the Cisco Email Security Appliance (WSA) proxy server, the access.log file. |
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) |
[OOTB] Cisco ISE syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) system received via Syslog. |
Cisco Netflow v5 |
[OOTB] NetFlow v5 |
netflow5 |
Designed for processing events from Cisco Netflow version 5. |
Cisco NetFlow v9 |
[OOTB] NetFlow v9 |
netflow9 |
Designed for processing events from Cisco Netflow version 9. |
Cisco Prime |
[OOTB] Cisco Prime syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Cisco Prime system version 3.10 received via syslog. |
Cisco Secure Email Gateway (SEG) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Citrix NetScaler |
[OOTB] Citrix NetScaler |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Citrix NetScaler 13.7 load balancer. |
Claroty Continuous Threat Detection |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
CloudPassage Halo |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Сodemaster Mirada |
[OOTB] Сodemaster Mirada syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Codemaster Mirada system received via syslog. |
Corvil Network Analytics |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Cribl Stream |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
CrowdStrike Falcon Host |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
CyberArk Privileged Threat Analytics (PTA) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
CyberPeak Spektr |
[OOTB] CyberPeak Spektr syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the CyberPeak Spektr system version 3 received via syslog. |
DeepInstinct |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Delinea Secret Server |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Digital Guardian Endpoint Threat Detection |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
BIND DNS server |
[OOTB] BIND Syslog [OOTB] BIND file |
Syslog regexp |
[OOTB] BIND Syslog is designed for processing events of the BIND DNS server received via Syslog. [OOTB] BIND file is designed for processing event logs of the BIND DNS server. |
Dovecot |
[OOTB] Dovecot Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Dovecot mail server received via Syslog. The event source is POP3/IMAP logs. |
Dragos Platform |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
EclecticIQ Intelligence Center |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Edge Technologies AppBoard and enPortal |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Eltex MES Switches |
[OOTB] Eltex MES Switches |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from Eltex network devices. |
Eset Protect |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
F5 BigIP Advanced Firewall Manager (AFM) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
FFRI FFR yarai |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
FireEye CM Series |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
FireEye Malware Protection System |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Forcepoint NGFW |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Forcepoint SMC |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Fortinet FortiGate |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
regexp |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Fortinet FortiGate |
[OOTB] FortiGate syslog KV |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from FortiGate firewalls via syslog. The event source is FortiGate logs in key-value format. |
Fortinet Fortimail |
[OOTB] Fortimail |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the FortiMail email protection system. The event source is Fortimail mail system logs. |
Fortinet FortiSOAR |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
FreeIPA |
[OOTB] FreeIPA |
json |
Designed for processing events from the FreeIPA system. The event source is Free IPA directory service logs. |
FreeRADIUS |
[OOTB] FreeRADIUS syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the FreeRADIUS system received via Syslog. The normalizer supports events from FreeRADIUS version 3.0. |
Gardatech GardaDB |
[OOTB] Gardatech GardaDB syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Gardatech GardaDB system received via syslog in a CEF-like format. |
Gardatech Perimeter |
[OOTB] Gardatech Perimeter syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Gardatech Perimeter system version 5.3 received via syslog. |
Gigamon GigaVUE |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
HAProxy |
[OOTB] HAProxy syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing logs of the HAProxy system. The normalizer supports events of the HTTP log, TCP log, Error log type from HAProxy version 2.8. |
Huawei Eudemon |
[OOTB] Huawei Eudemon |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from Huawei Eudemon firewalls. The event source is logs of Huawei Eudemon firewalls. |
Huawei USG |
[OOTB] Huawei USG Basic |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from Huawei USG security gateways via Syslog. |
IBM InfoSphere Guardium |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Ideco UTM |
[OOTB] Ideco UTM Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from Ideco UTM via Syslog. The normalizer supports events of Ideco UTM 14.7, 14.10. |
Illumio Policy Compute Engine (PCE) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Imperva Incapsula |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Imperva SecureSphere |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Orion Soft |
[OOTB] Orion Soft zVirt syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Orion Soft 3.1 virtualization system. |
Indeed PAM |
[OOTB] Indeed PAM syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Indeed PAM (Privileged Access Manager) version 2.6. |
Indeed SSO |
[OOTB] Indeed SSO |
xml |
Designed for processing events of the Indeed SSO (Single Sign-On) system. |
InfoWatch Traffic Monitor |
[OOTB] InfoWatch Traffic Monitor SQL |
sql |
Designed for processing events received by the connector from the database of the InfoWatch Traffic Monitor system. |
Intralinks VIA |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
IPFIX |
[OOTB] IPFIX |
ipfix |
Designed for processing events in the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) format. |
Juniper JUNOS |
[OOTB] Juniper - JUNOS |
regexp |
Designed for processing audit events received from Juniper network devices. |
Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack (KATA) |
[OOTB] KATA |
cef |
Designed for processing alerts or events from the Kaspersky Anti Targeted Attack activity log. |
Kaspersky CyberTrace |
[OOTB] CyberTrace |
regexp |
Designed for processing Kaspersky CyberTrace events. |
Kaspersky Endpoint Detection and Response (KEDR) |
[OOTB] KEDR telemetry |
json |
Designed for processing Kaspersky EDR telemetry tagged by KATA. The event source is kafka, EnrichedEventTopic |
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks |
[OOTB] KICS4Net v2.x |
cef |
Designed for processing events of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 2.x. |
Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks |
[OOTB] KICS4Net v3.x |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity for Networks version 3.x |
Kaspersky Security Center |
[OOTB] KSC |
cef |
Designed for processing Kaspersky Security Center events received via Syslog. |
Kaspersky Security Center |
[OOTB] KSC from SQL |
sql |
Designed for processing events received by the connector from the database of the Kaspersky Security Center system. |
Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server (KLMS) |
[OOTB] KLMS Syslog CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from Kaspersky Security for Linux Mail Server in CEF format via Syslog. |
Kaspersky Security Mail Gateway (KSMG) |
[OOTB] KSMG Syslog CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Kaspersky Secure Mail Gateway version 2.0 in CEF format via Syslog. |
Kaspersky Web Traffic Security (KWTS) |
[OOTB] KWTS Syslog CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from Kaspersky Web Traffic Security in CEF format via Syslog. |
Kaspersky Web Traffic Security (KWTS) |
[OOTB] KWTS (KV) |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in Kaspersky Web Traffic Security for Key-Value format. |
Kemptechnologies LoadMaster |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Kerio Control |
[OOTB] Kerio Control |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Kerio Control firewalls. |
KUMA |
[OOTB] KUMA forwarding |
json |
Designed for processing events forwarded from KUMA. |
Libvirt |
[OOTB] Libvirt syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Libvirt version 8.0.0 received via syslog. |
Lieberman Software ERPM |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Linux |
[OOTB] Linux audit and iptables Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Linux operating system. This normalizer will be removed from the OOTB set after the next release. If you are using this normalizer, you must migrate to the [OOTB] Linux audit and iptables Syslog v1 normalizer. |
Linux |
[OOTB] Linux audit and iptables Syslog v1 |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Linux operating system. |
Linux |
[OOTB] Linux audit.log file |
regexp |
Designed for processing security logs of Linux operating systems received via Syslog. |
MariaDB |
[OOTB] MariaDB Audit Plugin Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events coming from the MariaDB audit plugin over Syslog. |
Microsoft DHCP |
[OOTB] MS DHCP file |
regexp |
Designed for processing Microsoft DHCP server events. The event source is Windows DHCP server logs. |
Microsoft DNS |
[OOTB] DNS Windows |
regexp |
Designed for processing Microsoft DNS server events. The event source is Windows DNS server logs. |
Microsoft Exchange |
[OOTB] Exchange CSV |
csv |
Designed for processing the event log of the Microsoft Exchange system. The event source is Exchange server MTA logs. |
Microsoft IIS |
[OOTB] IIS Log File Format |
regexp |
The normalizer processes events in the format described at https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/http/iis-logging. The event source is Microsoft IIS logs. |
Microsoft Network Policy Server (NPS) |
[OOTB] Microsoft Products |
xml |
The normalizer is designed for processing events of the Microsoft Windows operating system. The event source is Network Policy Server events. |
Microsoft Sysmon |
[OOTB] Microsoft Products |
xml |
This normalizer is designed for processing Microsoft Sysmon module events. |
Microsoft Windows |
[OOTB] Microsoft Products |
xml |
The normalizer is designed for processing events of the Microsoft Windows operating system. |
Microsoft PowerShell |
[OOTB] Microsoft Products |
xml |
The normalizer is designed for processing events of the Microsoft Windows operating system. |
Microsoft SQL Server |
[OOTB] Microsoft SQL Server xml |
xml |
Designed for processing events of MS SQL Server versions 2008, 2012, 2014, 2016. |
Microsoft Windows Remote Desktop Services |
[OOTB] Microsoft Products |
xml |
The normalizer is designed for processing events of the Microsoft Windows operating system. The event source is the log at Applications and Services Logs - Microsoft - Windows - TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager - Operational |
Microsoft Windows XP/2003 |
[OOTB] SNMP. Windows {XP/2003} |
json |
Designed for processing events received from workstations and servers running Microsoft Windows XP, Microsoft Windows 2003 operating systems using the SNMP protocol. |
MikroTik |
[OOTB] MikroTik syslog |
regexp |
Designed for events received from MikroTik devices via Syslog. |
Minerva Labs Minerva EDR |
[OOTB] Minerva EDR |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Minerva EDR system. |
MySQL 5.7 |
[OOTB] MariaDB Audit Plugin Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events coming from the MariaDB audit plugin over Syslog. |
NetIQ Identity Manager |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
NetScout Systems nGenius Performance Manager |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Netskope Cloud Access Security Broker |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Netwrix Auditor |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Nextcloud |
[OOTB] Nextcloud syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for events of Nextcloud version 26.0.4 received via syslog. The normalizer does not save information from the Trace field. |
Nexthink Engine |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Nginx |
[OOTB] Nginx regexp |
regexp |
Designed for processing Nginx web server log events. |
NIKSUN NetDetector |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
One Identity Privileged Session Management |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Open VPN |
[OOTB] OpenVPN file |
regexp |
Designed for processing the event log of the OpenVPN system. |
Oracle |
[OOTB] Oracle Audit Trail |
sql |
Designed for processing database audit events received by the connector directly from an Oracle database. |
PagerDuty |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Palo Alto Cortex Data Lake |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Palo Alto Networks NGFW |
[OOTB] PA-NGFW (Syslog-CSV) |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from Palo Alto Networks firewalls received via Syslog in CSV format. |
Palo Alto Networks PANOS |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Penta Security WAPPLES |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Positive Technologies ISIM |
[OOTB] PTsecurity ISIM |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the PT Industrial Security Incident Manager system. |
Positive Technologies Network Attack Discovery (NAD) |
[OOTB] PTsecurity NAD |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from PT Network Attack Discovery (NAD) received via Syslog. |
Positive Technologies Sandbox |
[OOTB] PTsecurity Sandbox |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the PT Sandbox system. |
Positive Technologies Web Application Firewall |
[OOTB] PTsecurity WAF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the PTsecurity (Web Application Firewall) system. |
PostgreSQL pgAudit |
[OOTB] PostgreSQL pgAudit Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the pgAudit audit plug-n for PostgreSQL database received via Syslog. |
Proofpoint Insider Threat Management |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Proxmox |
[OOTB] Proxmox file |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Proxmox system version 7.2-3 stored in a file. The normalizer supports processing of events in access and pveam logs. |
PT NAD |
[OOTB] PT NAD json |
json |
Designed for processing events coming from PT NAD in json format. This normalizer supports events from PT NAD version 11.1, 11.0. |
QEMU - hypervisor logs |
[OOTB] QEMU - Hypervisor file |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the QEMU hypervisor stored in a file. QEMU 6.2.0 and Libvirt 8.0.0 are supported. |
QEMU - virtual machine logs |
[OOTB] QEMU - Virtual Machine file |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from logs of virtual machines of the QEMU hypervisor version 6.2.0, stored in a file. |
Radware DefensePro AntiDDoS |
[OOTB] Radware DefensePro AntiDDoS |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the DDOS Mitigator protection system received via Syslog. |
Reak Soft Blitz Identity Provider |
[OOTB] Reak Soft Blitz Identity Provider file |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Reak Soft Blitz Identity Provider system version 5.16, stored in a file. |
Recorded Future Threat Intelligence Platform |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
ReversingLabs N1000 Appliance |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Rubicon Communications pfSense |
[OOTB] pfSense Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the pfSense firewall received via Syslog. |
Rubicon Communications pfSense |
[OOTB] pfSense w/o hostname |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the pfSense firewall. The Syslog header of these events does not contain a hostname. |
SailPoint IdentityIQ |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Sendmail |
[OOTB] Sendmail syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of Sendmail version 8.15.2 received via syslog. |
SentinelOne |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Snort |
[OOTB] Snort 3 json file |
json |
Designed for processing events of Snort version 3 in JSON format. |
Sonicwall TZ |
[OOTB] Sonicwall TZ Firewall |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received via Syslog from the SonicWall TZ firewall. |
Sophos XG |
[OOTB] Sophos XG |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Sophos XG firewall. |
Squid |
[OOTB] Squid access Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Squid proxy server received via the Syslog protocol. |
Squid |
[OOTB] Squid access.log file |
regexp |
Designed for processing Squid log events from the Squid proxy server. The event source is access.log logs |
S-Terra VPN Gate |
[OOTB] S-Terra |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from S-Terra VPN Gate devices. |
Suricata |
[OOTB] Suricata json file |
json |
This package contains a normalizer for Suricata 7.0.1 events stored in a JSON file. The normalizer supports processing the following event types: flow, anomaly, alert, dns, http, ssl, tls, ftp, ftp_data, ftp, smb, rdp, pgsql, modbus, quic, dhcp, bittorrent_dht, rfb. |
ThreatConnect Threat Intelligence Platform |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
ThreatQuotient |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
TrapX DeceptionGrid |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Trend Micro Control Manager |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Trend Micro Deep Security |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Trend Micro NGFW |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Trustwave Application Security DbProtect |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Unbound |
[OOTB] Unbound Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the Unbound DNS server received via Syslog. |
UserGate |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format received from the UserGate system via Syslog. |
Varonis DatAdvantage |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Veriato 360 |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
VipNet TIAS |
[OOTB] Vipnet TIAS syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of ViPNet TIAS 3.8 received via Syslog. |
VMware ESXi |
[OOTB] VMware ESXi syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing VMware ESXi events (support for a limited number of events from ESXi versions 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0) received via Syslog. |
VMWare Horizon |
[OOTB] VMware Horizon - Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from the VMware Horizon 2106 system via Syslog. |
VMwareCarbon Black EDR |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Vormetric Data Security Manager |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Votiro Disarmer for Windows |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Wallix AdminBastion |
[OOTB] Wallix AdminBastion syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing events received from the Wallix AdminBastion system via Syslog. |
WatchGuard - Firebox |
[OOTB] WatchGuard Firebox |
Syslog |
Designed for processing WatchGuard Firebox events received via Syslog. |
Webroot BrightCloud |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Winchill Fracas |
[OOTB] PTC Winchill Fracas |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the Windchill FRACAS failure registration system. |
Zabbix |
[OOTB] Zabbix SQL |
sql |
Designed for processing events of Zabbix 6.4. |
ZEEK IDS |
[OOTB] ZEEK IDS json file |
json |
Designed for processing logs of the ZEEK IDS system in JSON format. The normalizer supports events from ZEEK IDS version 1.8. |
Zettaset BDEncrypt |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
Zscaler Nanolog Streaming Service (NSS) |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format. |
IT-Bastion – SKDPU |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format received from the IT-Bastion SKDPU system via Syslog. |
A-Real Internet Control Server (ICS) |
[OOTB] A-real IKS syslog |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of the A-Real Internet Control Server (ICS) system received via Syslog. The normalizer supports events from A-Real ICS version 7.0 and later. |
Apache web server |
[OOTB] Apache HTTP Server file |
regexp |
Designed for processing Apache HTTP Server 2.4 events stored in a file. The normalizer supports processing of events from the Application log in the Common or Combined Log formats, as well as the Error log. Expected format of the Error log events: "[%t] [%-m:%l] [pid %P:tid %T] [server\ %v] [client\ %a] %E: %M;\ referer\ %-{Referer}i" |
Apache web server |
[OOTB] Apache HTTP Server syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the Apache HTTP Server received via syslog. The normalizer supports processing of Apache HTTP Server 2.4 events from the Access log in the Common or Combined Log format, as well as the Error log. Expected format of the Error log events: "[%t] [%-m:%l] [pid %P:tid %T] [server\ %v] [client\ %a] %E: %M;\ referer\ %-{Referer}i" |
Lighttpd web server |
[OOTB] Lighttpd syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing Access events of the Lighttpd system received via syslog. The normalizer supports processing of Lighttpd version 1.4 events. Expected format of Access log events: $remote_addr $http_request_host_name $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" |
IVK Kolchuga-K |
[OOTB] Kolchuga-K Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the IVK Kolchuga-K system, version LKNV.466217.002, via Syslog. |
infotecs ViPNet IDS |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format received from the infotecs ViPNet IDS system via Syslog. |
infotecs ViPNet Coordinator |
[OOTB] VipNet Coordinator Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events from the ViPNet Coordinator system received via Syslog. |
Kod Bezopasnosti — Continent |
[OOTB][regexp] Continent IPS/IDS & TLS |
regexp |
Designed for processing events of Continent IPS/IDS device log. |
Kod Bezopasnosti — Continent |
[OOTB] Continent SQL |
sql |
Designed for getting events of the Continent system from the database. |
Kod Bezopasnosti SecretNet 7 |
[OOTB] SecretNet SQL |
sql |
Designed for processing events received by the connector from the database of the SecretNet system. |
Confident - Dallas Lock |
[OOTB] Confident Dallas Lock |
regexp |
Designed for processing events from the Dallas Lock 8 information protection system. |
CryptoPro NGate |
[OOTB] Ngate Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from the CryptoPro NGate system via Syslog. |
NT Monitoring and Analytics |
[OOTB] Syslog-CEF |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events in the CEF format received from the NT Monitoring and Analytics system via Syslog. |
BlueCoat proxy server |
[OOTB] BlueCoat Proxy v0.2 |
regexp |
Designed to process BlueCoat proxy server events. The event source is the BlueCoat proxy server event log. |
SKDPU NT Access Gateway |
[OOTB] Bastion SKDPU-GW |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events of the SKDPU NT Access gateway system received via Syslog. |
Solar Dozor |
[OOTB] Solar Dozor Syslog |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received from the Solar Dozor system version 7.9 via Syslog. The normalizer supports custom format events and does not support CEF format events. |
- |
[OOTB] Syslog header |
Syslog |
Designed for processing events received via Syslog. The normalizer parses the header of the Syslog event, the message field of the event is not parsed. If necessary, you can parse the message field using other normalizers. |