Contents
Analytics
KUMA provides extensive analytics on the data available to the program from the following sources:
- Events in storage
- Alerts
- Assets
- Accounts imported from Active Directory
- Data from collectors on the number of processed events
- Metrics
You can configure and receive analytics in the Dashboard, Reports, and Source status sections of the KUMA Console. Analytics are built by using only the data from tenants that the user can access.
The date format depends on the localization language selected in the application settings. Possible date format options:
- English localization: YYYY-MM-DD.
- Russian localization: DD.MM.YYYY.
Dashboard
In the Dashboard section, you can monitor the security status of your organization's network.
The dashboard is a set of widgets that display network security data analytics. You can view data only for those tenants to which you have access.
A selection of widgets used in the dashboard is called a layout. You can create layouts manually or use predefined layouts. You can edit widget settings in predefined layouts as necessary. By default, the dashboard displays the Alerts Overview predefined layout.
Only users with the Main administrator, Tenant administrator, Tier 2 analyst, and Tier 1 analyst roles can create, edit, or delete layouts. Users accounts with all roles can view layouts and set default layouts. If a layout is set as default, that layout is displayed for the account every time the user navigates to the Dashboard section. The selected default layout is saved for the current user account.
The information on the dashboard is updated in accordance with the schedule configured in layout settings. If necessary, you can force the update of the data.
For convenient presentation of information on the dashboard, you can enable TV mode. This mode lets you view the dashboard in full-screen mode in FullHD resolution. In TV mode, you can also configure a slide show display for the selected layouts.
Creating a dashboard layout
To create a layout:
- Open the KUMA Console and select the Dashboard section.
- Open the drop-down list in the top right corner of the Dashboard window and select Create layout.
The New layout window opens.
- In the Tenants drop-down list, select the tenants that will own the created layout and whose data will be used to fill the widgets of the layout.
The selection of tenants in this drop-down list does not matter if you want to create a universal layout (see below).
- In the Time period drop-down list, select the time period from which you want to get analytics:
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
You can select a date up to and including the current date. The date and time format depends on your browser settings. If the Date from or Date to field has a value and you have not edited the time value manually, when you select a date in the calendar, the Date from field is automatically populated with 00:00:00.000, and the Date to field with 23:59:59.999. If you have manually deleted the value in the Date from or Date to field, when you select a date in the calendar, the field is automatically populated with the current time. After you select a value in one of the fields, the focus switches to the other field. If your Date to is earlier than your Date from, this earlier value is automatically inserted into the Date from field.
- If you want to specify a relative period, select one of the available periods in the Relative period list on the right.
The period is calculated relative to the current time.
- If you want to specify a custom period, edit the value of the Date from and Date to fields.
You can enter an exact date and time in the DD.MM.YYYY HH:mm:ss.SSS format for the Russian localization and YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS for the English localization or a period relative to the current time as a formula. You can also combine these methods if necessary. If you do not specify milliseconds when entering the exact date, 000 is substituted automatically. If you have edited the time in the Date from or Date to fields, picking a date in the calendar does not change the time component.
In the relative period formulas, you can use the now parameter for the current date and time and the interval parameterization language: + (only in the Date to field), -, / (rounding to the nearest), as well as time units: y (year), M (month), w (week), d (day), h (hour), m (minute), s (second). For example, you can specify the period now-5d to get data for the last five days, or now/w to get data from the beginning of the first day of the current week (00:00:00:000 UTC) to the current time (now).
The Date from field is required, and its value cannot exceed the value of the Date from field, and also cannot be earlier than 1970-01-01 (if specifying an exact date or a relative period). The Date to cannot be earlier than the Date from. If you do not specify a value in the Date from field, now is specified automatically.
By default, the 1 day (now-1d) relative period is selected. The bounds of the period are inclusive: for example, for the Today time range, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000 UTC) of the current day to the current time (now) inclusive, and for the Yesterday period, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000 UTC) of the previous day to 00:00:00:000 UTC of the current day.
KUMA stores time values in UTC, but in the user interface time is converted to the time zone of your browser. This is relevant to the relative periods: Today, Yesterday, This week, and This month. For example, if the time zone in your browser is UTC+3, and you select Today as the data display period, data will be displayed for the period from 03:00:00.000 until now, not from 00:00:00.000 until now.
If you want to take your time zone into account when selecting a relative data display period, such as Today, Yesterday, This week, or This month, you need to manually add a time offset in the Date from and Date to fields (if a value other than now is specified) by adding or subtracting the correct number of hours. For example, if your browser's time zone is UTC+3 and you want to display data for Yesterday, you need to change Date from to now-1d/d-3h and Date to to now/d-3h. If you want to display data for the Today period, you only need to change the value in the Date from field to now/d-3h.
If you need results up to 23:59:59:999 UTC of yesterday, you can use an SQL query with a filter by Timestamp or specify an exact date and time.
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
- In the Refresh every drop-down list, select how often data should be updated in layout widgets:
- never — never refresh data in widgets of the layout
- 1 minute
- 5 minutes
- 15 minutes
- 1 hour (default)
- 3 hours
- 6 hours
- 12 hours
- 24 hours
- In the Add widget drop-down list, select the required widget and configure its settings. You can add multiple widgets. You can drag widgets around the window and resize them using the
 button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.
button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.The following limitations apply to widgets with the Pie chart, Bar chart, Line chart, Counter, and Date Histogram chart types:
- In
SELECTqueries, you can use extended event schema fields of "String", "Number", and "Float" types. - In
WHEREqueries, you can use all types of extended event schema fields ("String", "Number", "Float", "Array of strings", "Array of numbers", and "Array of floats").
For widgets with the Table chart type, in
SELECTqueries, you can use all types of extended event schema fields ("String", "Number", "Float", "Array of strings", "Array of numbers", and "Array of floats").You can do the following with widgets:
You can edit and delete a widget added to the layout by hovering over the widget, clicking the icon
 that appears, and then selecting Edit or Delete.
that appears, and then selecting Edit or Delete. - In
- In the Layout name field, enter a unique name for this layout. Must contain 1 to 128 Unicode characters.
- If necessary, click the
 icon on the right of the layout name field and select the check boxes next to the additional layout settings:
icon on the right of the layout name field and select the check boxes next to the additional layout settings:- Universal—if you select this check box, layout widgets display data from tenants that you select in the Selected tenants section in the menu on the left. This means that the data in the layout widgets will change based on your selected tenants without having to edit the layout settings. For universal layouts, tenants selected in the Tenants drop-down list are not taken into account.
If this check box is cleared, layout widgets display data from the tenants that are selected in the Tenants drop-down list in the layout settings. If any of the tenants selected in the layout are not available to you, their data will not be displayed in the layout widgets.
You cannot use the Active lists and context tables widget in universal layouts.
Universal layouts can only be created and edited by General administrators. Such layouts can be viewed by all users.
- Show CII-related data—if you select this check box, layout widgets will also show data on assets, alerts, and incidents related to critical information infrastructure (CII). In this case, these layouts will be available for viewing only by users whose settings have the Access to CII facilities check box selected.
If this check box is cleared, layout widgets will not display data on CII-related assets, alerts, and incidents, even if the user has access to CII objects.
- Universal—if you select this check box, layout widgets display data from tenants that you select in the Selected tenants section in the menu on the left. This means that the data in the layout widgets will change based on your selected tenants without having to edit the layout settings. For universal layouts, tenants selected in the Tenants drop-down list are not taken into account.
- Click Save.
The new layout is created and is displayed in the Dashboard section of the KUMA Console.
Page topSelecting a dashboard layout
To select a dashboard layout:
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the Dashboard window.
- Select the relevant layout.
The selected layout is displayed in the Dashboard section of the KUMA Console.
Page topSelecting a dashboard layout as the default
To set a dashboard layout as the default:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the Dashboard window.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant layout.
- Click the
 icon.
icon.
The selected layout is displayed on the dashboard by default.
Page topEditing a dashboard layout
To edit a dashboard layout:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the window.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant layout.
- Click the
 icon.
icon.The Customizing layout window opens.
- Make the necessary changes. The settings that are available for editing are the same as the settings available when creating a layout.
- Click the Save button.
The dashboard layout is edited and displayed in the Dashboard section of the KUMA Console.
If the layout is deleted or assigned to a different tenant while are making changes to it, an error is displayed when you click Save. The layout is not saved. Refresh the KUMA Console page to see the list of available layouts in the drop-down list.
Page topDeleting a dashboard layout
To delete layout:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the window.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant layout.
- Click the
 icon and confirm this action.
icon and confirm this action.
The layout is deleted.
Page topEnabling and disabling TV mode
It is recommended to create a separate user with the minimum required set of right to display analytics in TV mode.
To enable TV mode:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Click the
 button in the upper-right corner.
button in the upper-right corner.The Settings window opens.
- Move the TV mode toggle switch to the Enabled position.
- To configure the slideshow display of the layouts, do the following:
- Move the Slideshow toggle switch to the Enabled position.
- In the Timeout field, indicate how many seconds to wait before switching layouts.
- In the Queue drop-down list, select the layouts to view. If no layout is selected, the slideshow mode displays all layouts available to the user one after another.
- If necessary, change the order in which the layouts are displayed using the
 button to drag and drop them.
button to drag and drop them.
- Click the Save button.
TV mode will be enabled. To return to working with the KUMA Console, disable TV mode.
To disable TV mode:
- Open the KUMA Console and select the Dashboard section.
- Click the
 button in the upper-right corner.
button in the upper-right corner.The Settings window opens.
- Move the TV mode toggle switch to the Disabled position.
- Click the Save button.
TV mode will be disabled. The left part of the screen shows a pane containing sections of the KUMA Console.
When you make changes to the layouts selected for the slideshow, those changes will automatically be applied to the active slideshow sessions.
Page topPredefined dashboard layouts
KUMA comes with a set of predefined layouts: The default refresh period for predefined layouts is Never. You can edit these layouts as needed.
Predefined layouts
Layout name |
Description of widgets in the layout |
|---|---|
Alerts Overview |
|
Incidents Overview |
|
Network Overview |
|
[OOTB] KATA & EDR |
|
[OOTB] KSC |
|
[OOTB] KSMG |
|
[OOTB] KWTS |
|
Reports
You can configure KUMA to regularly generate reports about KUMA processes.
Reports are generated using report templates that are created and stored on the Templates tab of the Reports section.
Generated reports are stored on the Generated reports tab of the Reports section.
To save the generated reports in HTML and PDF formats, install the required packages on the device with the KUMA Core.
When deploying KUMA in a high availability version, the time zone of the Application Core server and the time in the user's browser may differ. This difference is manifested by the discrepancy between the time in reports generated by schedule and the data that the user can export from widgets. To avoid this discrepancy, it is recommended to configure the report generation schedule to take into account the difference between the users' time zone and UTC.
Report template
Report templates are used to specify the analytical data to include in the report, and to configure how often reports must be generated. Users with the General administrator, Tenant administrator, Tier 2 analyst, and Tier 1 analyst roles can create, edit, or delete report templates. Reports that were generated using report templates are displayed in the Generated reports tab.
Report templates are available in the Templates tab of the Reports section, where the table of existing templates is displayed. The table has the following columns:
- Name—the name of the report template.
You can sort the table by this column by clicking the title and selecting Ascending or Descending.
You can also search report templates by using the Search field that opens when you click the Name column title.
Regular expressions are used when searching for report templates.
- Schedule—the rate at which reports must be generated using the template. If the report schedule was not configured, the
disabledvalue is displayed. - Created by—the name of the user who created the report template.
- Updated—the date when the report template was last updated.
You can sort the table by this column by clicking the title and selecting Ascending or Descending.
- Last report—the date and time when the last report was generated based on the report template.
- Send by email—the check mark is displayed in this column for the report templates that notify users about generated reports via email notifications.
- Tenant—the name of the tenant that owns the report template.
You can click the name of the report template to open the drop-down list with available commands:
- Run report—use this option to generate report immediately. The generated reports are displayed on the Generated reports tab.
- Edit schedule—use this command to configure the schedule for generating reports and to define users that must receive email notifications about generated reports.
- Edit report template—use this command to configure widgets and the time period for extracting analytics.
- Duplicate report template—use this command to create a copy of the existing report template.
- Delete report template—use this command to delete the report template.
Creating report template
To create report template:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- Click the New template button.
The New report template window opens.
- In the Tenants drop-down list, select one or more tenants that will own the layout being created.
- In the Time period drop-down list, select the time period from which you want to get analytics:
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
You can select a date up to and including the current date. The date and time format depends on your browser settings. If the Date from or Date to field has a value and you have not edited the time value manually, when you select a date in the calendar, the Date from field is automatically populated with 00:00:00.000, and the Date to field with 23:59:59.999. If you have manually deleted the value in the Date from or Date to field, when you select a date in the calendar, the field is automatically populated with the current time. After you select a value in one of the fields, the focus switches to the other field. If your Date to is earlier than your Date from, this earlier value is automatically inserted into the Date from field.
- If you want to specify a relative period, select one of the available periods in the Relative period list on the right.
The period is calculated relative to the current time.
- If you want to specify a custom period, edit the value of the Date from and Date to fields.
You can enter an exact date and time in the DD.MM.YYYY HH:mm:ss.SSS format for the Russian localization and YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS for the English localization or a period relative to the current time as a formula. You can also combine these methods if necessary. If you do not specify milliseconds when entering the exact date, 000 is substituted automatically. If you have edited the time in the Date from or Date to fields, picking a date in the calendar does not change the time component.
In the relative period formulas, you can use the now parameter for the current date and time and the interval parameterization language: + (only in the Date to field), -, / (rounding to the nearest), as well as time units: y (year), M (month), w (week), d (day), h (hour), m (minute), s (second). For example, you can specify the period now-5d to get data for the last five days, or now/w to get data from the beginning of the first day of the current week (00:00:00:000 UTC) to the current time (now).
The Date from field is required, and its value cannot exceed the value of the Date from field, and also cannot be earlier than 1970-01-01 (if specifying an exact date or a relative period). The Date to cannot be earlier than the Date from. If you do not specify a value in the Date from field, now is specified automatically.
By default, the 1 day (now-1d) relative period is selected. The bounds of the period are inclusive: for example, for the Today time range, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000) of the current day to the current time (now) inclusive, and for the Yesterday period, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000) of the previous day to 00:00:00:000 of the current day.
KUMA stores time values in UTC, but in the user interface time is converted to the time zone of your browser. This is relevant to the relative periods: Today, Yesterday, This week, and This month. For example, if the time zone in your browser is UTC+3, and you select Today as the data display period, data will be displayed for the period from 03:00:00.000 until now, not from 00:00:00.000 until now.
If you want to take your time zone into account when selecting a relative data display period, such as Today, Yesterday, This week, or This month, you need to manually add a time offset in the Date from and Date to fields (if a value other than now is specified) by adding or subtracting the correct number of hours. For example, if your browser's time zone is UTC+3 and you want to display data for Yesterday, you need to change Date from to now-1d/d-3h and Date to to now/d-3h. If you want to display data for the Today period, you only need to change the value in the Date from field to now/d-3h.
If you need results up to 23:59:59:999 UTC of yesterday, you can use an SQL query with a filter by Timestamp or specify an exact date and time.
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
- In the Retention field, specify how long you want to store reports that are generated according to this template.
- In the Template name field, enter a unique name for the report template. Must contain 1 to 128 Unicode characters.
- In the Add widget drop-down list, select the required widget and configure its settings. You can add multiple widgets. You can drag widgets around the window and resize them using the
 button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.
button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.The following limitations apply to widgets with the Pie chart, Bar chart, Line chart, Counter, and Date Histogram chart types:
- In
SELECTqueries, you can use extended event schema fields of "String", "Number", and "Float" types. - In
WHEREqueries, you can use all types of extended event schema fields ("String", "Number", "Float", "Array of strings", "Array of numbers", and "Array of floats").
For widgets with the Table chart type, in
SELECTqueries, you can use all types of extended event schema fields ("String", "Number", "Float", "Array of strings", "Array of numbers", and "Array of floats").You can do the following with widgets:
You can edit and delete a widget added to the layout by hovering over the widget, clicking the icon
 that appears, and then selecting Edit or Delete.
that appears, and then selecting Edit or Delete. - In
- You can change logo in the report template by clicking the Upload logo button.
When you click the Upload logo button, the Upload window opens and lets you choose the image file for the logo. The image must be a .jpg, .png, or .gif file no larger than 3 MB.
The added logo is displayed in the report instead of KUMA logo.
- If necessary, select the Show CII-related data check box to display data on assets, alerts, and incidents related to critical information infrastructure (CII) in the layout widgets. In this case, these layouts will be available for viewing only by users whose settings have the Access to CII facilities check box selected.
If this check box is cleared, layout widgets will not display data on CII-related assets, alerts, and incidents, even if the user has access to CII objects.
- Click Save.
The new report template is created and is displayed on the Reports → Templates tab of the KUMA Console. You can run this report manually. If you want to have the reports generated automatically, you must configure the schedule for that.
Page topConfiguring report schedule
To configure the report schedule:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- In the report templates table, click the name of an existing report template and select Edit schedule in the drop-down list.
The Report settings window opens.
- If you want the report to be generated regularly:
- Turn on the Schedule toggle switch.
In the Recur every group of settings, define how often the report must be generated.
You can specify the frequency of generating reports by days, weeks, months, or years. Depending on the selected period, you should specify the time, day of the week, day of the month or the date of the report generation.
- In the Time field, enter the time when the report must be generated. You can enter the value manually or using the clock icon.
- Turn on the Schedule toggle switch.
- To select the report format and specify the report recipients, configure the following settings:
- In the Send to group of settings, click Add.
- In the Add emails window that opens, in the User group section, click Add group.
- In the field that appears, specify the email address and press Enter or click outside the entry field—the email address will be added. You can add more than one address. Reports are sent to the specified addresses every time you generate a report manually or KUMA generates a report automatically on schedule.
You should configure an SMTP connection so that generated reports can be forwarded by email.
If the recipients who received the report by email are KUMA users, they can download or view the report by clicking the links in the email. If the recipients are not KUMA users, they can follow the links but cannot log in to KUMA, so only attachments are available to them.
We recommend viewing HTML reports by clicking links in the web interface, because at some screen resolutions, the HTML report from the attachment may not be displayed correctly.
If you send an email without attachments, the recipients will have access to reports only by links and only with authorization in KUMA, without restrictions on roles or tenants.
- In the drop-down list, select the report format to send. Available formats: PDF, HTML, , Excel.
- Click Save.
Report schedule is configured.
Page topEditing report template
To edit report template:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- In the report templates table click the name of the report template and select Edit report template in the drop-down list.
The Edit report template window opens.
You can also open this window on the Reports → Generated reports tab by clicking the name of a generated report and selecting in the drop-down list Edit report template.
- Make the necessary changes:
- Change the list of tenants that own the report template.
- Update the time period from which you require analytics.
- Add widgets
- Change widgets positions by dragging them.
- Resize widgets using the
 button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.
button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget. - Edit widgets
- Delete widgets by hovering the mouse over them, clicking the
 icon that appears, and selecting Delete.
icon that appears, and selecting Delete. - In the field to the right from the Add widget drop-down list enter a new name of the report template. Must contain 1 to 128 Unicode characters.
- Change the report logo by uploading it using the Upload logo button. If the template already contains a logo, you must first delete it.
- Change how long reports generated using this template must be stored.
- If necessary, select or clear the Show CII-related data check box.
- Click Save.
The report template is updated and is displayed on the Reports → Templates tab of the KUMA Console.
Page topCopying report template
To create a copy of a report template:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- In the report templates table, click the name of an existing report template, and select Duplicate report template in the drop-down list.
The New report template window opens. The name of the widget is changed to
<Report template> - copy. - Make the necessary changes:
- Change the list of tenants that own the report template.
- Update the time period from which you require analytics.
- Add widgets
- Change widgets positions by dragging them.
- Resize widgets using the
 button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget.
button that appears when you hover the mouse over a widget. - Edit widgets
- Delete widgets by hovering the mouse over them, clicking the
 icon that appears, and selecting Delete.
icon that appears, and selecting Delete. - In the field to the right from the Add widget drop-down list enter a new name of the report template. Must contain 1 to 128 Unicode characters.
- Change the report logo by uploading it using the Upload logo button. If the template already contains a logo, you must first delete it.
- Click Save.
The report template is updated and is displayed on the Reports → Templates tab of the KUMA Console.
Page topDeleting report template
To delete report template:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- In the report templates table, click the name of the report template, and select Delete report template in the drop-down list.
A confirmation window opens.
- If you want to delete only the report template, click the Delete button.
- If you want to delete a report template and all the reports that were generated using that template, click the Delete with reports button.
The report template is deleted.
Page topGenerated reports
All reports are generated using report templates. Generated reports are available on the Generated reports tab of the Reports section and are displayed in the table with the following columns:
- Name—the name of the report template.
You can sort the table by this column by clicking the title and selecting Ascending or Descending.
- Time period—the time period for which the report analytics were extracted.
- Last report—date and time when the report was generated.
You can sort the table by this column by clicking the title and selecting Ascending or Descending.
- Tenant—name of the tenant that owns the report.
- User—name of the user who generated the report manually. If the report was generated by schedule, the value is blank. If the report was generated in KUMA lower than 2.1, the value is blank.
You can click the name of a report to open the drop-down list with available commands:
- Open report—use this command to open the report data window.
- Save as—use this command to save the generated report in the desired format. Available formats: HTML, PDF, CSV, split CSV, Excel. By default, 250 rows are displayed in all formats. At most 500 values can be displayed in tables in PDF and HTML formats. If you want to output more than 500 rows in a report, set your value for the LIMIT parameter in the SQL query and save the report in CSV format.
- Run report—use this option to generate report immediately. Refresh the browser window to see the newly generated report in the table.
- Edit report template—use this command to configure widgets and the time period for extracting analytics.
- Delete report—use this command to delete the report.
Viewing reports
To open report:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Generated reports.
- In the report table, click the name of the generated report, and select Open report in the drop-down list.
The new browser window opens with the widgets displaying report analytics. If a widget displays data on events, alerts, incidents, active lists, or context tables, you can click its header to open the corresponding section of the KUMA Console with an active filter and/or search query that is used to display data from the widget. Widgets are subject to default restrictions.
To download the data displayed on each widget in CSV format with UTF-8 encoding, press the CSV button. The downloaded file name has the format <widget name>_<download date (YYYYMMDD)>_<download time (HHMMSS)>.CSV.
To view the full data, download the report in the CSV format with the specified settings from the request.
- You can save the report in the desired format by using the Save as button.
Generating reports
You can generate report manually or configure a schedule to have it generated automatically.
To generate report manually:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Templates.
- In the report templates table, click a report template name and select Run report in the drop-down list.
You can also generate report from the Reports → Generated reports tab by clicking the name of an existing report and in the drop-down list selecting Run report.
The report is generated and is displayed on the Reports → Generated reports tab.
To generate reports automatically, configure the report schedule.
Page topSaving reports
To save the report in the desired format:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Generated reports.
- In the report table, click the name of the generated report, and in the drop-down list select Save as. Then select the desired format: HTML, PDF, CSV, split CSV, Excel.
The report is saved to the download folder configured in your browser.
You can also save the report in the desired format when you view it.
Page topDeleting reports
To delete report:
- Open the KUMA Console and select Reports → Generated reports.
- In the report table, click the name of the generated report, and in the drop-down list select Delete report.
A confirmation window opens.
- Click OK.
Widgets
Widgets let you monitor the operation of the application. Widgets are organized into widget groups, each one related to the analytics type they provide. The following widget groups and widgets are available in KUMA:
- Events—widget for creating analytics based on events.
- Active lists—widget for creating analytics based on active lists of correlators.
- Alerts—group for alert analytics.
The group includes the following widgets:
- Active alerts—number of alerts that have not been closed.
- Active alerts by tenant—number of unclosed alerts for each tenant.
- Alerts by tenant—number of alerts of all statuses for each tenant.
- Unassigned alerts—number of alerts that have the New status.
- Alerts by assignee—number of alerts with the Assigned status, grouped by account name.
- Alerts by status—number of alerts that have the New, Opened, Assigned, or Escalated status, grouped by status.
- Alerts by severity—number of unclosed alerts grouped by their severity.
- Alerts by rule—number of unclosed alerts grouped by correlation rule.
- Latest alerts—table with information about the last 10 unclosed alerts belonging to the tenants selected in the layout.
- Alerts distribution—number of alerts created during the period configured for the widget.
- Assets—group for analytics for assets from processed events. This group includes the following widgets:
- Affected assets—table with information about the level of importance of assets and the number of unclosed alerts they are associated with.
- Affected asset categories—categories of assets linked to unclosed alerts.
- Number of assets—number of assets that were added to KUMA.
- Assets in incidents by tenant—number of assets associated with unclosed incidents. The grouping is by tenant.
- Assets in alerts by tenant—number of assets associated with unclosed alerts, grouped by tenant.
- Incidents—group for incident analytics.
The group includes the following widgets:
- Active incidents—number of incidents that have not been closed.
- Unassigned incidents—number of incidents that have the Opened status.
- Incidents distribution—number of incidents created during the period configured for the widget.
- Incidents by assignee—number of incidents with the Assigned status, grouped by user account name.
- Incidents by status—number of incidents grouped by status.
- Incidents by severity—number of unclosed incidents grouped by their severity.
- Active incidents by tenant—number of unclosed incidents grouped by tenant available to the user account.
- All incidents—number of incidents of all statuses.
- All incidents by tenant—number of incidents of all statuses, grouped by tenant.
- Affected assets in incidents—number of assets associated with unclosed incidents.
- Affected assets categories in incidents—asset categories associated with unclosed incidents.
- Affected users in Incidents—users associated with incidents.
- Latest incidents—table with information about the last 10 unclosed incidents belonging to the tenants selected in the layout.
- Event sources—group for event source analytics. The group includes the following widgets:
- Top event sources by alerts number—number of unclosed alerts grouped by event source.
- Top event sources by convention rate—number of events associated with unclosed alerts. The grouping is by event source.
In some cases, the number of alerts generated by sources may be inaccurate. To obtain accurate statistics, it is recommended to specify the Device Product event field as unique in the correlation rule, and enable storage of all base events in a correlation event. However, correlation rules with these settings consume more resources.
- Users—group for analytics related to users from processed events. The group includes the following widgets:
- Affected users in alerts—number of accounts related to unclosed alerts.
- Number of AD users—number of Active Directory accounts received via LDAP during the period configured for the widget.
In the events table, in the event details area, in the alert window, and in the widgets, the names of assets, accounts, and services are displayed instead of the IDs as the values of the SourceAssetID, DestinationAssetID, DeviceAssetID, SourceAccountID, DestinationAccountID, and ServiceID fields. When exporting events to a file, the IDs are saved, but columns with names are added to the file. The IDs are also displayed when you point the mouse over the names of assets, accounts, or services.
Searching for fields with IDs is only possible using IDs.
Basics of managing widgets
The principle of data display in the widget depends on the type of the graph. The following graph types are available in KUMA:
- Pie chart (
 ).
). - Counter (
 ).
). - Table (
 ).
). - Bar chart (
 ).
). - Date Histogram (
 ).
). - Line chart.
- Stacked bar chart.
Basics of general widget management
The name of the widget is displayed in the upper left corner of the widgets. By clicking the link with the name of the widget about events, alerts, incidents, or active lists, you can go to the corresponding section of the KUMA Console.
A list of tenants for which data is displayed is located under the widget name.
In the upper right corner of the widget, the period for which data is displayed on the widget is indicated (for example, 30 days  ). Keep in mind that the data displayed in the dashboard may lag behind real time because of caching. You can view the date and time of the last update by hovering over the period icon.
). Keep in mind that the data displayed in the dashboard may lag behind real time because of caching. You can view the date and time of the last update by hovering over the period icon.
If the Show data for previous period setting is enabled for the widget, and the widget is displaying data for a relative period, the tooltip also displays the previous period. The previous period is calculated relative to the current period as start and end values of the current period minus the duration of the current period. For example, if data is updated daily and displayed for a month, but only the first 10 days of the month have passed, the previous period is taken to be the last 10 days of the previous month.
You can change the data display period for the widget by clicking the period icon and selecting an exact date or a relative period in the window that is displayed. If you want the widget to display data for the period selected for the layout, click the Reset button. Changing the displayed period on the layout also changes the period displayed in the widget.
The time in the widget is displayed in the local time zone set in the browser.
The CSV button is located to the left of the period icon. You can download the data displayed on the widget in CSV format (UTF-8 encoding). The downloaded file name has the format <widget name>_<download date (YYYYMMDD)>_<download time (HHMMSS)>.CSV.
The widget displays data for the period selected in widget or layout settings only for the tenants that are selected in widget or layout settings.
Basics of managing "Pie chart" graphs
A pie chart is displayed under the list of tenants. You can left-click the selected segment of the diagram to go to the relevant section of the KUMA Console. The data in that section is sorted in accordance with the filters and/or search query specified in the widget.
Under the period icon, you can see the number of events, active lists, assets, alerts, or incidents grouped by the selected criteria for the data display period.
Examples:
|
Basics of managing "Counter" graphs
Graphs of this type display the sum total of selected data.
Example: The Number of assets widget displays the total number of assets added to KUMA. |
Basics of managing "Table" graphs
Graphs of this type display data in a table format.
Example: In the Events widget, for which the SQL query |
Basics of managing "Bar chart" graphs
A bar chart is displayed below the list of tenants. You can left-click the selected diagram section to go to the Events section of the KUMA Console. The data in that section is sorted in accordance with the filters and/or search query specified in the widget. To the right of the chart, the same data is represented as a table.
Example: In the a Netflow top internal IPs widget for which the SQL query |
Basics of managing "Date Histogram" graphs
A date histogram is displayed below the list of tenants. You can left-click the selected section of the chart to go to the Events section of the KUMA Console with the relevant data. The data in that section is sorted in accordance with the filters and/or search query specified in the widget. To the right of the chart, the same data is represented as a table.
Example: In the Events widget, for which the SQL query |
Basics of managing "Line chart" graphs
A line chart is displayed below the list of tenants. You can left-click the selected section of the chart to go to the Events section of the KUMA Console with the relevant data. The data in that section is sorted in accordance with the filters and/or search query specified in the widget. To the right of the chart, the same data is represented as a table.
Example: In the Events widget, for which the SQL query |
Basics of managing "Stacked bar chart" graphs
A stacked bar chart with a legend is displayed below the list of tenants. The legend displays the names of categories by which the bars are sliced. To the left of each category is a check box that lets you hide or show the category. The number of bars in the chart corresponds to the number of values in the selected grouping. The bars have captions. The color of the corresponding category in the bar is assigned automatically. When you hover over the zones of the bars, a tooltip is displayed with the value and a description of the value. You can left-click the selected diagram section to go to the Events section of the KUMA Console.
The meaning of bar height depends on the Format setting:
- If the Absolute values format is configured, the height of the bars corresponds to the sum of the values of the measured figure.
- If the Relative values, % format is configured, all bars have the same height of 100%, and the relative heights of colored zones on the bars correspond to the ratios of the values.
If, when creating a custom widget based on the stacked bar chart, you selected the Show data for previous period option, and the standard value, category, metric aliases are used in the query, the chart displays previous-period data as separate bars. However, if instead of the standard metric, the query uses a custom metric calculation with non-standard aliases, the Show data for previous period is not taken into account when displaying the chart (see example queries below).
Examples: When creating a custom widget of the Stacked bar chart type based on an SQL query of an Events widget, the following rules apply:
However, you can manage the count by using standard aggregation functions ( Example 1: For the Events widget, the following SQL query is specified with standard aliases, and the Show data for previous period option was selected when creating the widget:
The X-axis stands for tenants (the field specified as the Next to each bar, an additional bar is displayed with historical data, if such data was received in the query response. Example 2: For the Events widget, the following SQL query is specified with custom metrics specified as the
The X-axis stands for tenants (the field specified as The additional bar with historical data is not displayed for a query with custom metrics, even if the Show data for previous period option was selected when creating the widget. Example 3: For the Events widget, the following SQL query is specified with standard aliases:
In contrast to the similar query in example 1, in this case, the X-axis stands for the types of events (the field specified as the Example 4: For the Events widget, the following SQL query is specified with standard aliases:
The chart displays the days of the month on the X axis (the field specified as the To create a similar chart with bars arranged by date and/or time, use a query with grouping and sorting by the following fields of the
We recommend using the Date Histogram to work with data that is arranged by date and/or time. |
Special considerations for displaying data in widgets
Limitations for the displayed data
For improved readability, KUMA has limitations on the data displayed in widgets depending on its type:
- Pie chart displays a maximum of 20 slices.
- Bar chart displays a maximum of 40 bars.
- Table displays a maximum of 500 entries.
- Date histogram displays a maximum of 365 days.
Data that exceeds the specified limitations is displayed in the widget in the Other category.
You can download the full data used for building analytics in the widget in CSV format.
Summing up the data
The format of displaying the total sum of data on date histogram, bar chart and pie chart depends on the locale:
- English locale: decades (every three digits) are separated by commas, the decimal part is separated by a period.
- Russian locale: decades (every three digits) are separated by spaces, the decimal part is separated by a comma.
Creating a widget
You can create a widget in a dashboard layout while creating or editing the layout.
To create a widget:
- Create a layout or switch to editing mode for the selected layout.
- Click Add widget.
- Select a widget type from the drop-down list.
This opens the widget settings window.
- Edit the widget settings.
- If you want to see how the data will be displayed in the widget, click Preview.
- Click Add.
The widget appears in the dashboard layout.
Page topEditing a widget
To edit widget:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the window.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant layout.
- Click the
 button.
button.The Customizing layout window opens.
- In the widget you want to edit, click
 .
. - Select Edit.
This opens the widget settings window.
- Edit the widget settings.
- Click Save in the widget settings window.
- Click Save in the Customizing layout window.
The widget is edited.
Page topDeleting a widget
To delete a widget:
- In the KUMA Console, select the Dashboard section.
- Expand the list in the upper right corner of the window.
- Hover the mouse cursor over the relevant layout.
- Click the
 button.
button.The Customizing layout window opens.
- In the widget you want to delete, click
 .
. - Select Delete.
- This opens a confirmation window; in that window, click OK.
- Click the Save button.
The widget is deleted.
Page top"Events" widget
You can use the Events widget to get analytics based on SQL queries.
When creating this widget, you must specify the settings described in the tables below.
Tab 
The following table lists the settings on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Graph |
Graph type. The following graph types are available:
|
Format |
Data display format: Absolute values or Relative values, %. The setting is available for a Stacked bar chart. If you select the Absolute values format, the heights of the bars correspond to the sum of the values of the measured indicator. If you select the Relative values, % format, all bars have the same height of 100%, and the relative heights of colored zones on the bars correspond to the ratios of indicator values. By default, Absolute values is selected. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Time period |
Period for which data is displayed in the widget. The default is As layout, meaning that data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. You can also specify a period for the widget in one of the following ways:
For details, see the Configuring a period subsection below. |
Show data for previous period |
Enable the display of data for two periods at the same time: for the current period and for the previous period. When using a Stacked bar chart, the Show data for previous period setting is taken into account if the query contains standard aliases: |
Storage |
Storage that is searched for events. The list displays the available spaces. You can select only one storage, but you can select one or more spaces. The values in the Storage field are independent of the selected tenants in the Tenant field. The field displays storages and spaces, like in the Events section. If the user does not have access rights to one or more spaces of the storage, the widget cannot display information; the user cannot edit the widget, but can duplicate the widget using the Duplicate button. Duplication does not depend on access rights to spaces. If a template is duplicated in widgets that have spaces specified that are not accessible to the user, the value in the Storage field is reset. Such widgets display an error: Access denied (Operation returns no results because of allowed and selected event spaces). To save the template, you need to specify spaces in widgets. In widgets that have spaces that are accessible to the user, the value of the Storage field is not reset and is saved when the template is duplicated. If the user's email address is included in the list of recipients of the scheduled report, the user gets the full version of the report, regardless of which spaces are accessible. |
SQL query field ( |
Query for filtering and searching for events manually. You can create a query in Builder by clicking For detailed information on creating an SQL query in the query constructor, see below. The following limitations apply:
|
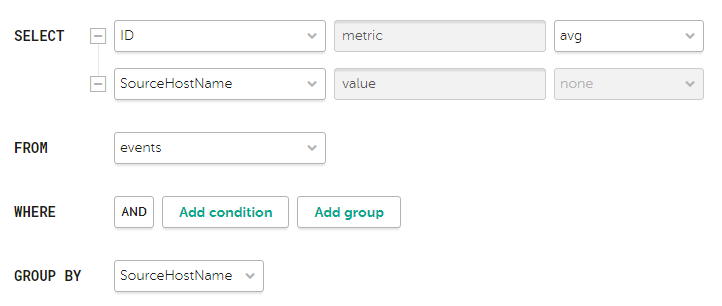
How to create a query in Builder
Example of search conditions in the query builder
Tab 
The following table lists the settings on the  tab.
tab.
The tab is displayed if on the  tab in the Graph field you have selected one of the following values: Bar chart, Line chart, Date Histogram.
tab in the Graph field you have selected one of the following values: Bar chart, Line chart, Date Histogram.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Y-min and Y-max |
Scale of the Y axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
X-min and X-max |
Scale of the X axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
Line-width |
Width of the line on the graph. This field is displayed for the "Line chart" graph type. |
Point size |
Point size on the graph. This field is displayed for the "Line chart" graph type. |
Tab 
The following table lists the settings on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Color |
The color used for displaying the information:
This setting is available for graphs such as Bar chart, Counter, Line chart, Date Histogram. |
Horizontal |
Makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical. When this option is enabled, when a widget displays a large amount of data, horizontal scrolling is not available and all available information is fit into the fixed size of the widget. If there is a lot of data to display, it is recommended to increase the widget size. |
Show total |
Shows sums total of the values. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Decimals |
Number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off. |
Period segments length |
Duration of the segments into which you want to divide the period. Available for graphs of the Date Histogram type. |
Scale |
Scale for displaying data. Available for a Stacked bar chart. The following values are possible:
The default is Linear. |
"Active lists" widget
You can use the Active lists widget to get analytics based on SQL queries.
When creating this widget, you must specify the settings described in the tables below.
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Graph |
Graph type. The following graph types are available:
|
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Correlator |
The name of the correlator that contains the active list for which you want to receive data. |
Active list |
The name of the active list for which you want to receive data. The same active list can be used by different correlators. However, a separate entity of the active list is created for each correlator. Therefore, the contents of the active lists used by different correlators differ even if the active lists have the same names and IDs. |
SQL query field |
This field lets you manually enter a query for filtering and searching active list data. The query structure is similar to that used in event search. When creating a query based on active lists, you must consider the following:
Special considerations apply when using aliases in SQL functions and SELECT, you can use double quotes and backticks: ", `. If you selected Counter as the graph type, aliases can contain Latin and Cyrillic characters, as well as spaces. When using spaces or Cyrillic, the alias must be enclosed in quotation marks: "An alias with a space", `Another alias`. When displaying data for the previous period, sorting by the count(ID) parameter may not work correctly. It is recommended to sort by the metric parameter. For example, SELECT count(ID) AS "metric", Name AS "value" FROM `events` GROUP BY Name ORDER BY metric ASC LIMIT 250. |
You can get the names of the tenants in the widget instead of their IDs.
Sample SQL queries for receiving analytics based on active lists:
|
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
This tab is displayed if on the  tab, in the Graph field, you have selected Bar chart.
tab, in the Graph field, you have selected Bar chart.
Description of parameters
Settings |
Description |
|---|---|
Y-min and Y-max |
Scale of the Y axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
X-min and X-max |
Scale of the X axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Color |
The color used for displaying the information:
|
Horizontal |
Makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical. When this setting is enabled, all available information is fitted into the configured widget size. If the amount of data is great, you can increase the size of the widget to display it optimally. |
Show total |
Shows sums total of the values. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
"Context tables" widget
You can use the Context tables widget to get analytics based on SQL queries.
When creating this widget, you must specify the settings described in the tables below.
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Graph |
Graph type. The following graph types are available:
|
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Correlator |
Name of the correlator that contains the context table for which you want to receive information. |
Context table |
Name of the context table for which you want to receive information. The same context table can be used in multiple correlators. However, a separate entity of the context table is created for each correlator. Therefore, the contents of the context tables used by different correlators are different even if the context tables have the same name and ID. |
SQL query field |
This field lets you manually enter a query for filtering and searching context table data. By default, for each widget type, the field contains a query that obtains the context table schema and the key by key fields. The query structure is similar to that used in event search. When creating a query based on context tables, you must consider the following:
Special considerations when using aliases in SQL functions and |
You can get the names of the tenants in the widget instead of their IDs.
Sample SQL queries for receiving analytics based on active lists:
|
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
This tab is displayed if on the  tab, in the Graph field, you have selected Bar chart.
tab, in the Graph field, you have selected Bar chart.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Y-min and Y-max |
Scale of the Y axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
X-min and X-max |
Scale of the X axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
Tab 
The following table lists the settings that must be specified on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Settings |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Color |
The color used for displaying the information:
|
Horizontal |
Makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical. When this setting is enabled, all available information is fitted into the configured widget size. If the amount of data is great, you can increase the size of the widget to display it optimally. |
Show total |
Shows sums total of the values. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
"Assets" customized widget
You can use the Assets → Customized widget to get advanced asset analytics from processed events using the query builder. In the query, you must specify the asset field and the corresponding condition or set of conditions by which you want the assets to be counted (Y-axis). You can also specify one or more additional conditions (categories) to be used for comparing the number of assets for each field.
When creating the custom widget for assets, you must specify the settings described in the tables below.
Tab 
The following table describes the settings on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Graph |
Graph type. The following graph types are available:
|
Format |
This setting is available for charts of the Stacked bar chart type. Data display format: Absolute values or Relative values, %. If you select the Absolute values format, the heights of the bars correspond to the sum of the values of the measured indicator. If you select the Relative values, % format, all bars have the same height of 100%, and the relative heights of colored zones on the bars correspond to the ratios of indicator values. By default, Absolute values is selected. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Asset category |
The asset category for which the widget is displaying data. |
Search in uncategorized assets |
This setting lets you display assets that do not have a category. This check box is cleared by default. |
Select axes group of settings |
|
Y-axis |
Required setting. Asset field and the condition or set of conditions specified for this field, that define how assets are to be counted. |
Y-axis category |
Category for the selected field. Not used for a graph of the Counter type. This setting is optional for Y-axis fields whose values are enumerations (can be selected from a finite list of values). For all other fields, this parameter is required. |
Group by tenant |
This setting is available for charts of the Stacked bar chart type. Enables additional grouping of assets by tenant. If the check box is selected, assets on the chart are broken up along the X-axis into bars corresponding to individual tenants. If the check box is cleared, all assets are displayed on the same bar. This check box is cleared by default. |
Tab 
The following table describes the settings on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Show total |
This setting is available for charts of the Pie chart type. Enables the display of totals in the chart, in addition to the selected categories. If this check box is enabled, the sum of the values of all specified categories is displayed in the center of the pie chart and in the legend in a separate Total column. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Color |
This setting is available for charts of the Counter type. The color used for displaying the information:
|
Horizontal |
Makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical. When this option is enabled, when a widget displays a large amount of data, horizontal scrolling is not available and all available information is fit into the fixed size of the widget. If there is a lot of data to display, it is recommended to increase the widget size. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Decimals |
Number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off. |
Scale |
Available for a Stacked bar chart. Scale for displaying data. The following values are possible:
The default is Linear. |
Other widgets
This section describes the settings of all widgets except the Events and Active lists widgets.
The set of parameters available for a widget depends on the type of graph that is displayed on the widget. The following graph types are available in KUMA:
- Pie chart (
 ).
). - Counter (
 ).
). - Table (
 ).
). - Bar chart (
 ).
). - Date Histogram (
 ).
). - Line chart.
- Stacked bar chart.
Settings for pie charts
The following table below lists the settings of a Pie chart.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Time period |
Period for which data is displayed in the widget. The default is As layout, meaning that data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. You can also specify a period for the widget in one of the following ways:
For details, see the Configuring a period subsection below. |
Show total |
Shows sums total of the values. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Decimals |
Number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off. |
Settings for counters
The following table below lists the settings of a Counter.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Time period |
Period for which data is displayed in the widget. The default is As layout, meaning that data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. You can also specify a period for the widget in one of the following ways:
For details, see the Configuring a period subsection below. |
Settings for tables
The following table below lists the settings of a Table.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Time period |
Period for which data is displayed in the widget. The default is As layout, meaning that data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. You can also specify a period for the widget in one of the following ways:
For details, see the Configuring a period subsection below. |
Show data for previous period |
Enabling the display of data for the current and previous periods simultaneously. |
Color |
The color used for displaying the information:
|
Decimals |
Number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off. |
Settings for Bar charts, Stacked bar charts, and Date Histograms
The table below lists the settings for the Bar chart and Date Histogram type graphs located on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Y-min and Y-max |
Scale of the Y axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
X-min and X-max |
Scale of the X axis. Negative values can be displayed on chart axes. This is due to the scaling of charts on the widget and can be fixed by setting zero as the minimum chart values instead of Auto. |
Decimals |
Number of decimals to which the displayed value must be rounded off. |
The table below lists the settings for the Bar chart, Stacked bar chart, and Date Histogram type graphs located on the  tab.
tab.
Description of parameters
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of the widget. |
Description |
Description of the widget. |
Tenant |
The tenant for which data is displayed in the widget. You can select multiple tenants. By default, data is displayed for tenants selected in layout settings. |
Time period |
Period for which data is displayed in the widget. The default is As layout, meaning that data is displayed for the period selected for the layout. You can also specify a period for the widget in one of the following ways:
For details, see the Configuring a period subsection below. |
Show data for previous period |
Enables the display of data simultaneously for the current and previous periods. |
Color |
The color used for displaying the information:
|
Horizontal |
Makes the histogram horizontal instead of vertical. When this setting is enabled, all available information is fitted into the configured widget size. If the amount of data is great, you can enlarge the widget to better fit the data. |
Show total |
Shows sums total of the values. |
Show legend |
Displays a legend for the analytics. The toggle switch is turned on by default. |
Show nulls in legend |
Displays parameters with a null value in the legend for analytics. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Period segments length |
Duration of the segments into which you want to divide the period. Available for graphs of the Date Histogram type. |
Configuring a period
For graphs such as Pie chart, Counter, Table, Bar chart, Stacked bar chart, Date Histogram, you can configure the period for displaying data in the widget using the Period setting. By default, the data display period of the widget is the same as the data display period of the dashboard.
To configure the data display period, do one of the following:
- If necessary, change the date and time in the Time period setting in one of the following ways:
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
You can select a date up to and including the current date. The date and time format depends on your browser settings. If the Date from or Date to field has a value and you have not edited the time value manually, when you select a date in the calendar, the Date from field is automatically populated with 00:00:00.000, and the Date to field with 23:59:59.999. If you have manually deleted the value in the Date from or Date to field, when you select a date in the calendar, the field is automatically populated with the current time. After you select a value in one of the fields, the focus switches to the other field. If your Date to is earlier than your Date from, this earlier value is automatically inserted into the Date from field.
- If you want to specify a relative period, select one of the available periods in the Relative period list on the right.
The period is calculated relative to the current time.
- If you want to specify a custom period, edit the value of the Date from and Date to fields.
You can enter an exact date and time in the DD.MM.YYYY HH:mm:ss.SSS format for the Russian localization and YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS for the English localization or a period relative to the current time as a formula. You can also combine these methods if necessary. If you do not specify milliseconds when entering the exact date, 000 is substituted automatically. If you have edited the time in the Date from or Date to fields, picking a date in the calendar does not change the time component.
In the relative period formulas, you can use the now parameter for the current date and time and the interval parameterization language: + (only in the Date to field), -, / (rounding to the nearest), as well as time units: y (year), M (month), w (week), d (day), h (hour), m (minute), s (second). For example, you can specify the period now-5d to get data for the last five days, or now/w to get data from the beginning of the first day of the current week (00:00:00:000 UTC) to the current time (now).
The Date from field is required, and its value cannot exceed the value of the Date from field, and also cannot be earlier than 1970-01-01 (if specifying an exact date or a relative period). The Date to cannot be earlier than the Date from. If you do not specify a value in the Date from field, now is specified automatically.
KUMA stores time values in UTC, but in the user interface time is converted to the time zone of your browser. This is relevant to the relative periods: Today, Yesterday, This week, and This month. For example, if the time zone in your browser is UTC+3, and you select Today as the data display period, data will be displayed for the period from 03:00:00.000 until now, not from 00:00:00.000 until now.
If you want to take your time zone into account when selecting a relative data display period, such as Today, Yesterday, This week, or This month, you need to manually add a time offset in the Date from and Date to fields (if a value other than now is specified) by adding or subtracting the correct number of hours. For example, if your browser's time zone is UTC+3 and you want to display data for Yesterday, you need to change Date from to now-1d/d-3h and Date to to now/d-3h. If you want to display data for the Today period, you only need to change the value in the Date from field to now/d-3h.
If you need results up to 23:59:59:999 UTC of yesterday, you can use an SQL query with a filter by Timestamp or specify an exact date and time.
The bounds of the period are inclusive: for example, for the Today time range, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000 UTC) of the current day to the current time (now) inclusive, and for the Yesterday period, events are displayed from the beginning (00:00:00:000 UTC) of the previous day to 00:00:00:000 UTC of the current day. You can view the date and time of the last data update and the exact period for which the data is displayed by hovering over the period icon in the widget.
If the Show data for previous period setting is enabled for the widget, and the widget is displaying data for a relative period, the tooltip also displays the previous period. The previous period is calculated relative to the current period as start and end values of the current period minus the duration of the current period. For example, if data is updated daily and displayed for a month, but only the first 10 days of the month have passed, the previous period is taken to be the last 10 days of the previous month.
- If you want to specify an exact date, in the calendar on the left, select the start and end date of the period and click Apply.
- If you want the widget to display data for the period selected for the layout, click the Reset button. Changing the displayed period on the layout also changes the period displayed in the widget.
Displaying tenant names in "Active list" type widgets
If you want the names of tenants to be displayed in 'Active list' type widgets instead of tenant IDs, in correlation rules of the correlator, configure the function for populating the active list with information about the corresponding tenant.
The configuration process proceeds in stages:
- Export the list of tenants.
- Create a dictionary of the Table type.
- Import the list of tenants obtained at step 1 into the dictionary created at step 2 of these instructions.
- Add a local variable with the dict function for mapping the tenant name to tenant ID to the correlation rule.
Example:
- Variable:
TenantName - Value:
dict ('<Name of the previously created dictionary with tenants>', TenantID)
- Variable:
- Add a Set action to the correlation rule, which writes the value of the previously created variable to the active list in the <key>-<value> format. As the key, specify the field of the active list (for example,
Tenant), and in the value field, specify the variable (for example,$TenantName).
When this rule triggers, the name of the tenant mapped by the dict function to the ID in the tenant dictionary is placed in the active list. When creating widgets based on active lists, the widget displays the name of the tenant instead of the tenant ID.
Page top
 )
) .
.