Contents
Solution architecture
Kaspersky Container Security components are deployed based on the images included in the distribution kit. The table below shows which images correspond to which solution components.
Kaspersky Container Security components
Component |
Image |
Component function |
|---|---|---|
ClickHouse DBMS |
clickhouse |
Managing ClickHouse databases for storing and processing informational messages from agents. |
PostgreSQL DBMS |
postgresql |
Managing databases using tools for analyzing and optimizing query parsing and query engines.
|
Middleware |
middleware |
Implements the data processing business logic of the server component of the solution and exposes a REST API to the graphical user interface of Kaspersky Container Security. |
Event Broker |
event-broker |
Ensuring communication between various elements of the distributed solution system. |
Image Handler, client scanner |
image-handler |
Processing scan jobs using vulnerability and malware scanners: starting scan jobs, scanning objects, aggregating and publishing scan results. |
Scanner server |
scanner-server |
Managing the scanner server, which is used to store the vulnerabilities database and the image layer cache, as well as to support the image handler. |
Licensing module |
licenses |
Manage functionalities provided under the license. |
File storage |
minio |
Managing the storage for storing and distributing to users the files that the solution generates. |
Multi-threaded event-based key-value cache storage |
memcached |
Managing the cache storage for keys and values that the solution receives as part of events. |
File server with updates for private corporate networks |
updates |
Delivery of updates when the solution is deployed. |
Solution interface |
nginx |
Functioning of the Kaspersky Container Security graphical user interface. |
Agent Broker |
agent-broker |
Ensuring communication between various elements of the distributed solution system. |
Agents |
node-agent kube-agent |
Maintaining security on the nodes in accordance with configured security policies and integration with the orchestrator. |
The solution includes the following main components:
- Kaspersky Container Security Middleware
- Kaspersky Container Security Agents
- Kaspersky Container Security Scanner
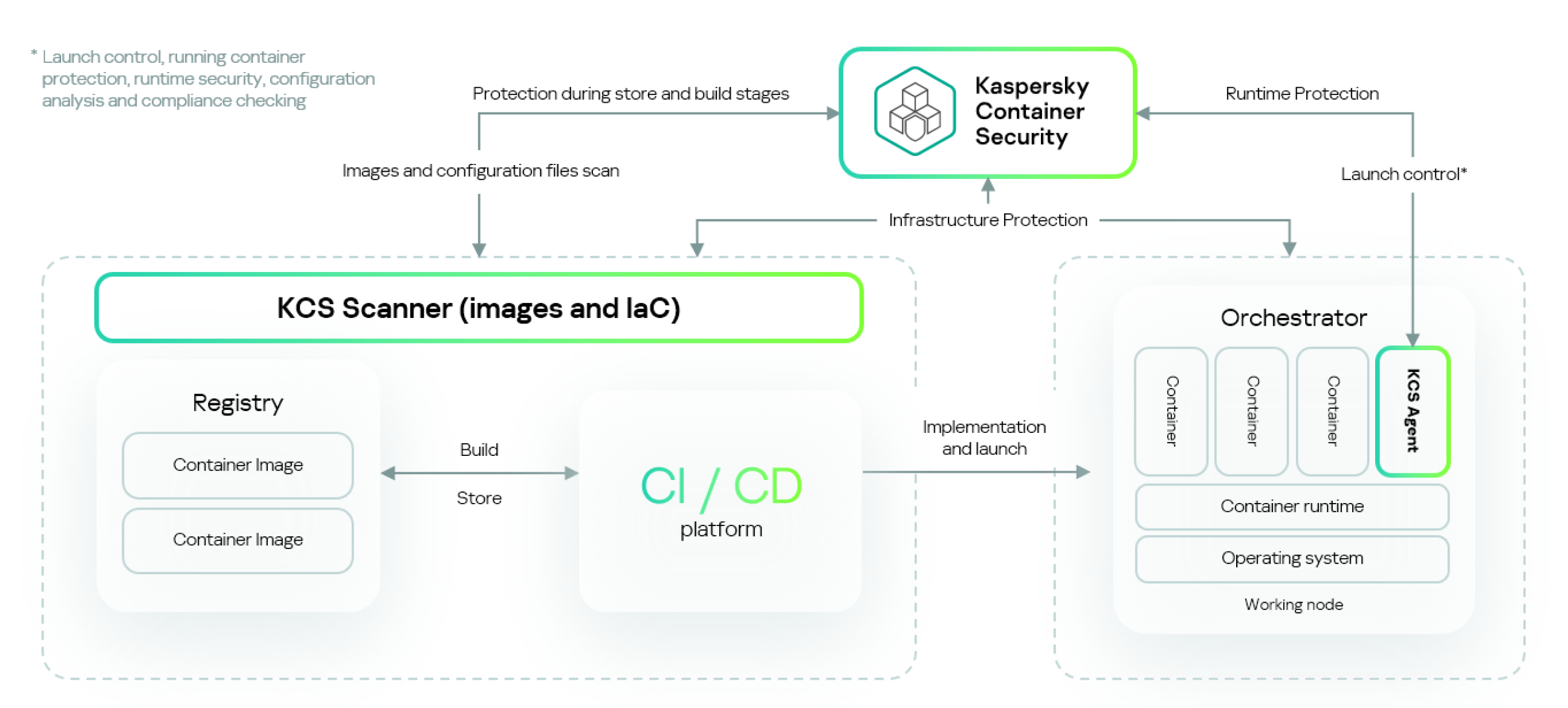
Overall architecture scheme of Kaspersky Container Security
Kaspersky Container Security can be deployed in a public or private corporate network.
Middleware
The Kaspersky Container Security middleware has the following functions:
- Provides an interface for interactive management of the solution (Management Console).
- Ensures integration with external software components (SIEM, CI, image registries, LDAP, Telegram, email) and the receipt of information from them.
- Coordinates the operation of other solution components.
- Ensures the creation and management of security policies.
- Displays the results of solution operations.
Agents
Kaspersky Container Security Agents (hereinafter also referred to as "agents") are a solution component that runs as a containerized application and provides security on nodes in accordance with configured security policies, in particular:
- Runtime security of containers running on the nodes.
- Network interaction between pods and applications inside containers.
- Integration with the orchestration platform and flow of data necessary for analysis of the orchestrator configuration and its components.
- Startup of containers from trusted images to prevent unverified images from running.
Agents are installed on all nodes of clusters and all clusters that need protection. Kaspersky Container Security works with two types of agents: cluster protection agents (csp-kube-agent) and node protection agents (csp-node-agent). Together they form groups of agents. A separate group of agents is created for each cluster. Multiple groups of agents can be created for one installation of the solution.
Agents do not inject their executable code into containers in monitored clusters.
If the cluster contains no agents, some of the solution functionality is unavailable (for example, runtime policies, resource monitoring).
Page topScanner
Scanner is a Kaspersky Container Security software component that scans objects in real time to assess their security and detect known vulnerabilities, malware, signs of sensitive data, and misconfigurations. The scanner lets you conduct security checks based on active security policies.
Kaspersky Container Security employs the following types of scanners:
- Vulnerability scanner based on the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database
- File threat scanner within the File Threat Protection component
- Configuration file scanner
- Sensitive data (secrets) scanner
About object scanning
Kaspersky Container Security checks objects deployed in the solution during the scanning process. The scanning process searches for and analyzes threats and security risks associated with objects in the solution. Object scans must be performed regularly to keep track of emerging security threats.
When scanning, Kaspersky Container Security identifies the following security threats:
- Vulnerabilities
- Malware.
- Misconfigurations
- Sensitive data
- Non-compliance with security policy requirements
Scanning process
The scanner receives scan jobs through the image handler. The image handler is a module deployed in the Kaspersky Container Security infrastructure that forwards scan jobs to the scanner and receives the scan results from the scanner.
When scan jobs are forwarded, the current status of the scanner is determined as one of the following:
- Free — the scanner is not processing objects and can accept a job from the image handler application if requested.
- Busy — the scanner is currently processing a scan job. A new job from the image handler application is put in the queue.
The scan job queue includes all forwarded scan jobs and is generated in the following cases:
- An image registry scan is manually started.
- An image registry scan is automatically started.
- A bulk scan of cluster objects is started.
Jobs in the scan queue receive the following statuses:
- Pending — status assigned by default when a job is created.
- In progress — the job is being processed by the image handler.
- Parsing results — the solution processes the job scanning results to display them in the interface.
- Error— scan job failed.
- Finished — the results of the scan job are available.
Scan jobs from the queue are submitted to the image handler in the order of their receipt. A scan job then goes to a scanner with Free status and is scanned for security issues. The scan results are sent back to the image handler. The scan job is considered completed and finished if scanning results are received. If a scan job was performed three or more times but received no results, the scan job is given the Error status.
When scanning many large objects, the solution may be slower to display scan results in the user interface. You may have to wait up to several minutes for the results to appear. During this time, the scan jobs are displayed in the Scanners section with the Parsing results status.
If you want to speed up the processing of scan results, you can allocate more resources to the scan job handler by updating the variables in Helm Chart (for more details, see Scaling).
When an error occurs, the solution displays an error message that consists of a code and a text message (for example, HNDL-004: scan time out).
Error messages are displayed in English. Examples of messages and their meanings are listed in the table below.
Examples of possible error messages when running scan jobs
After scanning, the solution displays the scan results. If security threats are detected in an object, Kaspersky Container Security prompts you to perform one of the following actions:
- Delete the security threat.
- Accept the risk.
Requirements to third-party application passwords
Kaspersky Container Security operates using specific third-party services. The following solution components are included in the distribution kit:
- S3 compatible file storage
- ClickHouse DBMS
- PostgreSQL DBMS
- Multi-threaded event-based key-value cache storage Memcached
The parameters for deployment of these components are specified in the values.yaml configuration file in the Helm Chart package.
Passwords for these components have the following requirements:
- The minimum password length is 8 characters.
- Passwords must not contain the following special characters: ' and ".
Passwords are specified in the following variables in the configuration file:
MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORDfor S3-compatible file storage.CLICKHOUSE_PASSWORD,CLICKHOUSE_WRITE_PASSWORDandCLICKHOUSE_READ_PASSWORDfor ClickHouse.POSTGRES_PASSWORDfor PostgreSQL.MEMCACHED_PASSWORDfor the Memcached cache storage.