Contents
- Deploying Network Agent and the security application
- Initial deployment
- Configuring installers
- Installation packages
- MSI properties and transform files
- Deployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
- General information about the remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
- Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
- Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
- Running stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
- Options for manual installation of applications
- Remote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
- Managing device restarts in the remote installation task
- Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of an anti-virus application
- Removing incompatible third-party security applications
- Using tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
- Monitoring the deployment
- Configuring installers
- Virtual infrastructure
- Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
- Initial deployment
Deploying Network Agent and the security application
To manage devices in an organization, you have to install Network Agent on each of them. Deployment of distributed Kaspersky Security Center on corporate devices normally begins with installation of Network Agent on them.
In Microsoft Windows XP, Network Agent might not perform the following operations correctly: downloading updates directly from Kaspersky servers (as a distribution point); functioning as a KSN proxy server (as a distribution point); and detecting third-party vulnerabilities (if Vulnerability and Patch Management is used).
Initial deployment
If a Network Agent has already been installed on a device, remote installation of applications on that device is performed through this Network Agent. The distribution package of an application to be installed is transferred over communication channels between Network Agents and Administration Server, along with the installation settings defined by the administrator. To transfer the distribution package, you can use relay distribution nodes, that is, distribution points, multicast delivery, etc. For more details on how to install applications on managed devices with Network Agent already installed, see below in this section.
You can perform initial installation of Network Agent on devices running Windows, using one of the following methods:
- With third-party tools for remote installation of applications.
- With Windows group policies: using standard Windows management tools for group policies.
- In forced mode, using special options in the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center.
- By sending device users links to stand-alone packages generated by Kaspersky Security Center. Stand-alone packages are executable modules that contain the distribution packages of selected applications with their settings defined.
- Manually, by running application installers on devices.
On platforms other than Microsoft Windows, you have to perform initial installation of Network Agent on managed devices either through the existing third-party tools, or manually, by sending users an archive with a pre-configured distribution package. You can upgrade Network Agent to a new version or install other Kaspersky applications on non-Windows platforms, using Network Agents (already installed on devices) to perform remote installation tasks. In this case, installation is identical to that on devices running Microsoft Windows.
When selecting a method and a strategy for deployment of applications on a managed network, you must consider a number of factors (partial list):
- Configuration of the corporate network
- Total number of devices
- Presence of Windows domains on the managed network, possibility to modify Active Directory group policies in those domains
- Awareness of the user account(s) with local administrator rights on devices on which initial deployment of Kaspersky applications has been planned (i.e., availability of a domain user account with local administrator rights, or presence of unified local user accounts with administrator rights on those devices)
- Connection type and bandwidth of network channels between the Administration Server and MSP client networks, as well as the bandwidth of channels inside those networks
- Security settings applied on remote devices at the start of deployment (such as use of UAC and Simple File Sharing mode)
Configuring installers
Before starting deployment of Kaspersky applications on a network, you must specify the installation settings, that is, those defined during the application installation. When installing Network Agent, you should specify, at a minimum, an address for connection to the Administration Server and the proxy settings; some advanced settings may also be required. Depending on the installation method that you have selected, you can define settings in different ways. In the simplest case (manual interactive installation on a selected device), all relevant settings can be defined through the user interface of the Installer, so, in some cases, initial deployment can even be performed by sending users a link to the Network Agent distribution package together with the settings (Administration Server address, etc.) that the user must enter in the Installer interface.
This method is not recommended for use since it is inconvenient for users, entailing a high risk of errors when defining settings manually; it is also non-usable with non-interactive silent installation of applications on device groups. In general, the administrator must specify values for settings in centralized mode; those values can subsequently be used for creation of stand-alone packages. Stand-alone packages are self-extracting archives that contain distribution packages with settings defined by the administrator. Stand-alone packages can be located on resources that allow both downloading by end users (for example, on Kaspersky Security Center Web Server) and non-interactive installation on selected networked devices.
Page topInstallation packages
The first and main method of defining the installation settings of applications is all-purpose and thus suitable for all installation methods, both with Kaspersky Security Center tools, and with most third-party tools. This method consists of creating installation packages of applications in Kaspersky Security Center.
Installation packages are generated using the following methods:
- Automatically, from specified distribution packages, on the basis of included descriptors (files with the kud extension that contain rules for installation and results analysis, and other information)
- From the executable files of installers or from installers in Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) format, for standard or supported applications
Generated installation packages are organized hierarchically as folders with subfolders and files. In addition to the original distribution package, an installation package contains editable settings (including the installer's settings and rules for processing such cases as necessity of restarting the operating system in order to complete installation), as well as minor auxiliary modules.
Values of installation settings that are specific for a selected application to be supported can be specified in the Administration Console user interface when creating an installation package (more settings can be found in the properties of an installation package that has already been created). When performing remote installation of applications through Kaspersky Security Center tools, installation packages are delivered to target devices so that running the installer of an application makes all administrator-defined settings available for it. When using third-party tools for installation of Kaspersky applications, you only have to ensure the availability of the entire installation package on the target device, that is, the availability of the distribution package and its settings. Installation packages are created and stored by Kaspersky Security Center in a dedicated subfolder of the shared data folder.
Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.
For instructions about using this configuration method for Kaspersky applications before deployment through third-party tools, see section "Deployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows."
Immediately after Kaspersky Security Center installation, a few installation packages are automatically generated; they are ready for installation and include Network Agent packages and security application packages for Microsoft Windows.
In some cases, using installation packages for deployment of applications on an MSP client network implies the need to create installation packages on virtual Servers that correspond to MSP clients. Creating installation packages on virtual Servers allows you to use different installation settings for different MSP clients. In the first instance, this is useful when handling Network Agent installation packages since Network Agents deployed on the networks of different MSP clients use different addresses to connect to the Administration Server. Actually, the connection address determines the Server to which Network Agent connects.
In addition to the possibility to create new installation packages immediately on a virtual Administration Server, the main operation mode for installation packages on virtual Administration Servers is the "distribution" of installation packages from the primary Administration Server to virtual ones. You can distribute selected (or all) installation packages to selected virtual Administration Servers (including all Servers within a selected administration group) using the corresponding Administration Server task. Also, you can select the list of installation packages of the primary Administration Server when creating a new virtual Administration Server. The packages that you have selected will be immediately distributed to a newly created virtual Administration Server.
When distributing an installation package, its contents are not copied entirely. The file repository on a virtual Administration Server, which corresponds to the installation package being distributed, only stores files of settings that are specific for that virtual Server. The main part of the installation package (including the distribution package of the application being installed) remains unchanged; it is stored only in the primary Administration Server repository. This allows you to increase the system performance dramatically and reduce the required disk volume. When handling installation packages distributed to virtual Administration Servers (i.e., when running remote installation tasks or creating stand-alone installation packages), the data from the original installation package of the primary Administration Server is "merged" with the settings files, which correspond to the distributed package on the virtual Administration Server.
Although the license key for an application can be set in the installation package properties, it is advisable to avoid this license distribution method because it is easy to accidentally obtain read access to files in the folder. You should use automatically distributed license keys or installation tasks for license keys.
Page topMSI properties and transform files
Another way of configuring installation on Windows platform is to define MSI properties and transform files. This method can be used when performing installation through third-party tools intended for installers in Microsoft Installer format, as well as when performing installation through Windows group policies using standard Microsoft tools or other third-party tools designed for handling Windows group policies.
Page topDeployment with third-party tools for remote installation of applications
When any tools for remote installation of applications (such as Microsoft System Center) are available in an organization, it is convenient to perform initial deployment by using those tools.
The following actions must be performed:
- Select the method for configuring installation that best suits the deployment tool to be used.
- Define the mechanism for synchronization between the modification of the settings of installation packages (through the Administration Console interface) and the operation of selected third-party tools used for deployment of applications from installation package data.
General information about the remote installation tasks in Kaspersky Security Center
Kaspersky Security Center provides a broad range of methods for remote installation of applications, which are implemented as remote installation tasks. You can create a remote installation task both for a specified administration group and for specific devices or a selection of devices (such tasks are displayed in Administration Console, in the Tasks folder). When creating a task, you can select installation packages (those of Network Agent and / or another application) to be installed within this task, as well as specify certain settings that define the method of remote installation.
Tasks for administration groups affect both devices included in a specified group and all devices in all subgroups within that administration group. A task covers devices of secondary Administration Servers included in a group or any of its subgroups if the corresponding setting is enabled in the task.
Tasks for specific devices refresh the list of client devices at each run in accordance with the selection contents at the moment the task starts. If a selection includes devices that have been connected to secondary Administration Servers, the task will run on those devices, too.
To ensure a successful operation of a remote installation task on devices connected to secondary Administration Servers, you must use the distribution task to distribute installation packages used by your task to corresponding secondary Administration Servers in advance.
Page topDeployment using group policies of Microsoft Windows
It is recommended that you perform the initial deployment of Network Agents through Microsoft Windows group policies if the following conditions are met:
- This device is member of an Active Directory domain.
- Access to the domain controller is granted with the administrator rights, which allow you to create and modify Active Directory group policies.
- Configured installation packages can be moved to the network hosting target managed devices (to a shared folder that is available for reading by all target devices).
- The deployment scheme allows you to wait for the next routine restart of target devices before starting deployment of Network Agents on them (or you can force a Windows group policy to be applied to those devices).
This deployment scheme consists of the following:
- The application distribution package in Microsoft Installer format (MSI package) is located in a shared folder (a folder where the LocalSystem accounts of target devices have read permissions).
- In the Active Directory group policy, an installation object is created for the distribution package.
- The installation scope is set by specifying the organizational unit (OU) and / or the security group, which includes the target devices.
- The next time a target device logs in to the domain (before device users log in to the system), all installed applications are checked for the presence of the required application. If the application is not found, the distribution package is downloaded from the resource specified in the policy and is then installed.
An advantage of this deployment scheme is that assigned applications are installed on target devices while the operating system is loading, that is, even before the user logs in to the system. Even if a user with sufficient rights removes the application, it will be reinstalled at the next launch of the operating system. This deployment scheme's shortcoming is that changes made by the administrator to the group policy will not take effect until the devices are restarted (if no additional tools are involved).
You can use group policies to install both Network Agent and other applications if their respective installers are in Windows Installer format.
Besides, when you select this deployment method, you have to assess the load on the file resource from which files will be copied to target devices after you apply the Windows group policy. You also have to choose the method of delivering the configured installation package to that resource, as well as the method of synchronizing the relevant changes in its settings.
Handling Microsoft Windows policies through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
This deployment method is only available if access to the controller of the domain, which contains the target devices, is possible from the Administration Server device, while the shared folder of the Administration Server (the one storing installation packages) is accessible for reading from target devices. Owing to the above reasons, this deployment method is not viewed as applicable to MSP.
Unassisted installation of applications through policies of Microsoft Windows
The administrator can create objects required for installation in a Windows group policy on his or her own behalf. In this case, you have to upload the packages to a stand-alone file server and provide a link to them.
The following installation scenarios are possible:
- The administrator creates an installation package and sets up its properties in Administration Console. Then the administrator copies the entire EXEC subfolder of this package from the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center to a folder on a dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization.
- The administrator downloads the application distribution package (including that of Network Agent) from the internet and uploads it to the dedicated file resource of the organization. The group policy object provides a link to the MSI file of this package stored in a subfolder on the dedicated file resource of the organization. The installation settings are defined by configuring the MSI properties or by configuring MST transform files.
Forced deployment through the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center
To perform initial deployment of Network Agents or other applications, you can force installation of selected installation packages by using the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center—provided that each device has a user account(s) with local administrator rights and at least one device with Network Agent installed acts as a distribution point in each subnet.
In this case, you can specify target devices either explicitly (with a list), or by selecting the Kaspersky Security Center administration group to which they belong, or by creating a selection of devices based upon a specific criterion. The installation start time is defined by the task schedule. If the Run missed tasks setting is enabled in the task properties, the task can be run either immediately after target devices are turned on, or when they are moved to the target administration group.
Forced installation consists of delivery of installation packages to distribution points, subsequent copying of files to the admin$ resource on each of the target devices, and remote registration of supporting services on those devices. Delivery of installation packages to distribution points is performed through a Kaspersky Security Center feature that ensures network interaction. The following conditions must be met in this case:
- Target devices are accessible from the distribution point side.
- Name resolution for target devices function properly on the network.
- The administrative shares (admin$) remain enabled on target devices.
- The Server system service is running on target devices (by default, it is running).
- The following ports are open on target devices to allow remote access through Windows tools: TCP 139, TCP 445, UDP 137, and UDP 138.
- On target devices running Microsoft Windows XP, Simple File Sharing mode is disabled.
- On target devices, the access sharing and security model are set as Classic – local users authenticate as themselves, it can be in no way Guest only – local users authenticate as Guest.
- Target devices are members of the domain, or uniform accounts with administrator rights are created on target devices in advance.
Devices in workgroups can be adjusted in accordance with the above requirements by using the riprep.exe utility, which is described on Kaspersky Technical Support website.
During installation on new devices that have not yet been allocated to any of the Kaspersky Security Center administration groups, you can open the remote installation task properties and specify the administration group to which devices will be moved after Network Agent installation.
When creating a group task, keep in mind that each group task affects all devices in all nested groups within a selected group. Therefore, you must avoid duplicating installation tasks in subgroups.
Automatic installation is a simplified way to create tasks for forced installation of applications. To do this, open the administration group properties, open the list of installation packages and select the ones that must be installed on devices in this group. As a result, the selected installation packages will be automatically installed on all devices in this group and all of its subgroups. The time interval over which the packages will be installed depends on the network throughput and the total number of networked devices.
To allow forced installation, you should make sure that distribution points are present in each of the isolated subnets hosting target devices.
Note that this installation method places a significant load on devices acting as distribution points. Therefore, it is recommended that you select powerful devices with high-performance storage units as distribution points. Moreover, the free disk space in the partition with the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit folder must exceed, by many times, the total size of the distribution packages of installed applications.
Page topRunning stand-alone packages created by Kaspersky Security Center
The above-described methods of initial deployment of Network Agent and other applications cannot always be implemented because it is not possible to meet all of the applicable conditions. In such cases, you can create a common executable file called a stand-alone installation package through Kaspersky Security Center, using installation packages with the relevant installation settings that have been prepared by the administrator. A stand-alone installation package can be published either on an internal Web Server (included in Kaspersky Security Center) if this is deemed reasonable (outside access to that Web Server has been configured for target device users), or on an exclusively deployed Web Server included in Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console. You can also copy stand-alone packages to another Web Server.
You can use Kaspersky Security Center to send selected users an email message containing a link to the stand-alone package file on the currently used Web Server, prompting them to run the file (either in interactive mode, or with the "-s" key for silent installation). You can attach the stand-alone installation package to an email message and then send it to the users of devices that have no access to the Web Server. The administrator can also copy the stand-alone package to an external device, deliver it to a relevant device, and then run it later.
You can create a stand-alone package from a Network Agent package, a package of another application (for example, the security application), or both. If the stand-alone package has been created from Network Agent and another application, installation starts with Network Agent.
When creating a stand-alone package with Network Agent, you can specify the administration group to which new devices (those that have not been allocated to any of the administration groups) will be automatically moved when Network Agent installation completes on them.
Stand-alone packages can run in interactive mode (by default), displaying the result for installation of applications they contain, or they can run in silent mode (when run with the key "-s"). Silent mode can be used for installation from scripts, for example, from scripts configured to run after an operating system image is deployed. The result of installation in silent mode is determined by the return code of the process.
Page topOptions for manual installation of applications
Administrators or experienced users can install applications manually in interactive mode. They can use either original distribution packages or installation packages generated from them and stored in the shared folder of Kaspersky Security Center. By default, installers run in interactive mode and prompt users for all required values. However, when running the process setup.exe from the root of an installation package with the key "-s", the installer will be running in silent mode and with the settings that have been defined when configuring the installation package.
When running setup.exe from the root of an installation package, the package will first be copied to a temporary local folder, and then the application installer will be run from the local folder.
Page topRemote installation of applications on devices with Network Agent installed
If an operable Network Agent connected to the primary Administration Server (or to any of its secondary Servers) is installed on a device, you can upgrade Network Agent on this device, as well as install, upgrade, or remove any supported applications through Network Agent.
You can enable this option by selecting the Using Network Agent check box in the properties of the remote installation task.
If this check box is selected, installation packages with installation settings defined by the administrator will be transferred to target devices over communication channels between Network Agent and the Administration Server.
To optimize the load on the Administration Server and minimize traffic between the Administration Server and the devices, it is useful to assign distribution points on every remote network or in every broadcasting domain (see sections About distribution points and Building a structure of administration groups and assigning distribution points). In this case, installation packages and the installer settings are distributed from the Administration Server to target devices through distribution points.
Moreover, you can use distribution points for broadcasting (multicast) delivery of installation packages, which allows reducing network traffic significantly when deploying applications.
When transferring installation packages to target devices over communication channels between Network Agents and the Administration Server, all installation packages that have been prepared for transfer will also be cached in the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1093\.working\FTServer folder. When using multiple large installation packages of various types and involving a large number of distribution points, the size of this folder may increase dramatically.
Files cannot be deleted from the FTServer folder manually. When original installation packages are deleted, the corresponding data will be automatically deleted from the FTServer folder.
All data received on the distribution points side are saved to the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\1103\$FTClTmp folder.
Files cannot be deleted from the $FTClTmp folder manually. As tasks using data from this folder complete, the contents of this folder will be deleted automatically.
Because installation packages are distributed over communication channels between Administration Server and Network Agents from an intermediate repository in a format optimized for network transfers, no changes are allowed in installation packages stored in the original folder of each installation package. Those changes will not be automatically registered by Administration Server. If you need to modify the files of installation packages manually (although you are recommended to avoid this scenario), you must edit any of the settings of an installation package in Administration Console. Editing the settings of an installation package in Administration Console causes Administration Server to update the package image in the cache that has been prepared for transfer to target devices.
Page topManaging device restarts in the remote installation task
Devices often need a restart to complete the remote installation of applications (particularly on Windows).
If you use the remote installation task of Kaspersky Security Center, in the Add Task Wizard or in the properties window of the task that has been created (Operating system restart section), you can select the action to perform when a restart is required:
- Do not restart the device. In this case, no automatic restart will be performed. To complete the installation, you must restart the device (for example, manually or through the device management task). Information about the required restart will be saved in the task results and in the device status. This option is suitable for installation tasks on servers and other devices where continuous operation is critical.
- Restart the device. In this case, the device is always restarted automatically if a restart is required for completion of the installation. This option is useful for installation tasks on devices that provide for regular pauses in their operation (shutdown or restart).
- Prompt user for action. In this case, the restart reminder is displayed on the screen of the client device, prompting the user to restart it manually. Some advanced settings can be defined for this option: text of the message for the user, the message display frequency, and the time interval after which a restart will be forced (without the user's confirmation). The Prompt user for action is the most suitable for workstations where users need a possibility of selecting the most convenient time for a restart.
Suitability of databases updating in an installation package of an anti-virus application
Before starting the protection deployment, you must keep in mind the possibility of updating anti-virus databases (including modules of automatic patches) shipped together with the distribution package of the security application. It is useful to update the databases in the installation package of the application before starting the deployment (for example, by using the corresponding command in the context menu of a selected installation package). This will reduce the number of restarts required for completion of protection deployment on target devices. If your remote installation involves installation packages that have been relayed to virtual Servers from the primary Administration Server, you only have to update databases in the original package on the primary Server. In this case, you do not have to update databases in relayed packages on virtual Servers.
Page topRemoving incompatible third-party security applications
Installation of Kaspersky security applications through Kaspersky Security Center may require removal of third-party software incompatible with the application being installed. There are two main ways of removing the third-party applications.
Automatic removal of incompatible applications by using the installer
When you run the installer, it shows a list of applications that are incompatible with a Kaspersky application:
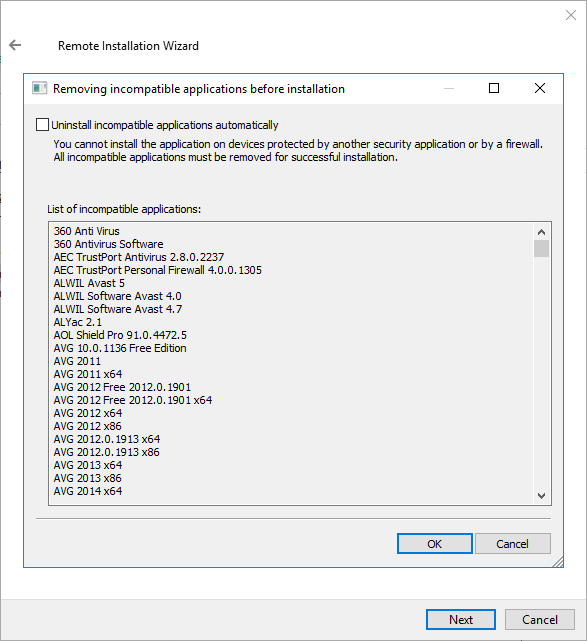
The list of incompatible applications that is displayed in the Remote Installation Wizard
Kaspersky Security Center detects incompatible software. Accordingly, you can select the Uninstall incompatible applications automatically check box to continue installation. If you clear this check box and do not uninstall the incompatible software, the error occurs and the Kaspersky application is not installed.
Automatic removal of incompatible applications is supported by various types of installation.
Removing incompatible applications through a dedicated task
To remove incompatible applications, use the Uninstall application remotely task. This task should be run on devices before the security application installation task. For example, in the installation task you can select On completing another task as the schedule type where the other task is Uninstall application remotely.
This method of uninstallation is useful when the security application installer cannot properly remove an incompatible application.
Page topUsing tools for remote installation of applications in Kaspersky Security Center for running relevant executable files on managed devices
Using the New Package Wizard, you can select any executable file and define the settings of the command line for it. For this you can add to the installation package either the selected file itself or the entire folder in which this file is stored. Then you must create the remote installation task and select the installation package that has been created.
While the task is running, the specified executable file with the defined settings of the command prompt will be run on target devices.
If you use installers in Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) format, Kaspersky Security Center analyzes the installation results by means of standard tools.
If the Vulnerability and Patch Management license is available, Kaspersky Security Center (when creating an installation package for any supported application in the corporate environment) also uses rules for installation and analysis of installation results that are in its updatable database.
Otherwise, the default task for executable files waits for the completion of the running process, and of all its child processes. After completion of all of the running processes, the task will be completed successfully regardless of the return code of the initial process. To change such behavior of this task, before creating the task, you have to manually modify the .kpd files that were generated by Kaspersky Security Center in the folder of the newly created installation package and its subfolders.
For the task not to wait for the completion of the running process, set the value of the Wait setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] Wait=0 |
For the task to wait only for the completion of the running process on Windows, not for the completion of all child processes, set the value of the WaitJob setting to 0 in the [SetupProcessResult], section, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult] WaitJob=0 |
For the task to complete successfully or return an error depending on the return code of the running process, list successful return codes in the [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes], section, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] 0= 3010= |
In this case, any code other than those listed will result in an error returned.
To display a string with a comment on the successful completion of the task or an error in the task results, enter brief descriptions of errors corresponding to return codes of the process in the [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] and [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] sections, for example:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_SuccessCodes] 0= Installation completed successfully 3010=A restart is required to complete the installation [SetupProcessResult_ErrorCodes] 1602=Installation canceled by the user 1603=Fatal error during installation |
To use Kaspersky Security Center tools for managing the device restart (if a restart is required to complete an operation), list the return codes of the process that indicate that a restart must be performed, in the [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] section:
Example: [SetupProcessResult_NeedReboot] 3010= |
Monitoring the deployment
To monitor the Kaspersky Security Center deployment and make sure that a security application and Network Agent are installed on managed devices, you have to check the traffic light in the Deployment section. This traffic light is located in the workspace of the Administration Server node in the main window of Administration Console. The traffic light reflects the current deployment status. The number of devices with Network Agent and security applications installed is displayed next to the traffic light. When any installation tasks are running, you can monitor their progress here. If any installation errors occur, the number of errors is displayed here. You can view the details of any error by clicking the link.
You can also use the deployment schema in the workspace of the Managed devices folder on the Groups tab. The chart reflects the deployment process, showing the number of devices without Network Agent, with Network Agent, or with Network Agent and a security application.
For more details on the progress of the deployment (or the operation of a specific installation task) open the results window of the relevant remote installation task: Right-click the task and select Results in the context menu. The window displays two lists: the upper one contains the task statuses on devices, while the lower one contains task events on the device that is currently selected in the upper list.
Information about deployment errors are added to the Kaspersky Event Log on Administration Server. Information about errors is also available in the corresponding selection of events in the Reports and notifications folder, the Events subfolder.
Page topConfiguring installers
This section provides information about the files of Kaspersky Security Center installers and the installation settings, as well as recommendations on how to install Administration Server and Network Agent in silent mode.
General information
Installers of Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 components (Administration Server, Network Agent, and Administration Console) are built on Windows Installer technology. An MSI package is the core of an installer. This format of packaging allows using all of the advantages provided by Windows Installer: scalability, availability of a patching system, transformation system, centralized installation through third-party solutions, and transparent registration with the operating system.
Installation in silent mode (with a response file)
The installers of Administration Server and Network Agent have the feature of working with the response file (ss_install.xml), where the parameters for installation in silent mode without user participation are integrated. The ss_install.xml file is located in the same folder as the MSI package; it is used automatically during installation in silent mode. You can enable the silent installation mode with the command line key "/s".
An overview of an example run follows:
setup.exe /s |
Before you start the installer in silent mode, read the End User License Agreement (EULA). If the Kaspersky Security Center distribution kit does not include a TXT file with the text of the EULA, you can download the file from the Kaspersky website.
The ss_install.xml file is an instance of the internal format of parameters of the Kaspersky Security Center installer. Distribution packages contain the ss_install.xml file with the default parameters.
Please do not modify ss_install.xml manually. This file can be modified through the tools of Kaspersky Security Center when editing the parameters of installation packages in Administration Console.
To modify the response file for Administration Server installation:
- Open the Kaspersky Security Center distribution package. If you use a full package EXE file, then unpack it.
- Form the Server folder, open the command line, and then run the following command:
setup.exe /r ss_install.xml
The Kaspersky Security Center installer starts.
- Follow the Wizard's steps to configure the Kaspersky Security Center installation.
When you complete the Wizard, the response file is automatically modified according to the new settings that you specified.
Installation of Network Agent in silent mode (without a response file)
You can install Network Agent with a single .msi package, specifying the values of MSI properties in the standard way. This scenario allows Network Agent to be installed by using group policies. To avoid conflicts between parameters defined through MSI properties and parameters defined in the response file, you can disable the response file by setting the property DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE=1. An example of a run of the Network Agent installer with an .msi package is as follows.
Installation of Network Agent in non-interactive mode requires acceptance of the terms of the End User License Agreement. Use the EULA=1 parameter only if you have fully read, understand and accept the terms of the End User License Agreement.
Example:
|
You can also define the installation parameters for an .msi package by preparing the response file in advance (one with an .mst extension). This command appears as follows:
Example:
|
You can specify several response files in a single command.
Partial installation configuration through setup.exe
When running installation of applications through setup.exe, you can add the values of any properties of MSI to the MSI package.
This command appears as follows:
Example: /v"PROPERTY_NAME1=PROPERTY_VALUE1 PROPERTYNAME2=PROPERTYVALUE2" |
Administration Server installation parameters
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Administration Server. All of the parameters are optional, except for EULA and PRIVACYPOLICY.
Parameters of Administration Server installation in non-interactive mode
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement (required) |
|
PRIVACYPOLICY |
Acceptance of the terms of the Privacy Policy (required) |
|
INSTALLATIONMODETYPE |
Type of Administration Server installation |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Application installation folder |
String value. |
ADDLOCAL |
List of components to install (separated by commas) |
CSAdminKitServer, NAgent, CSAdminKitConsole, NSAC, MobileSupport, KSNProxy, SNMPAgent, GdiPlusRedist, Microsoft_VC90_CRT_x86, Microsoft_VC100_CRT_x86. Minimum list of components sufficient for proper Administration Server installation:
|
NETRANGETYPE |
Network size |
|
SRV_ACCOUNT_TYPE |
Way of specifying the user for the operation of the Administration Server service |
|
SERVERACCOUNTNAME |
User name for the service |
String value. |
SERVERACCOUNTPWD |
User password for the service |
String value. |
DBTYPE |
Database type |
|
MYSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of MySQL or MariaDB server |
String value. |
MYSQLSERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server |
Numerical value. |
MYSQLDBNAME |
Name of MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MYSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to MySQL or MariaDB server database |
String value. |
MSSQLCONNECTIONTYPE |
Type of use of MSSQL database |
|
MSSQLSERVERNAME |
Full name of SQL Server instance |
String value. |
MSSQLDBNAME |
Name of SQL Server database |
String value. |
MSSQLAUTHTYPE |
Method of authentication for connection to SQL Server |
|
MSSQLACCOUNTNAME |
User name for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
MSSQLACCOUNTPWD |
User password for connection to SQL Server in SQLServer mode |
String value. |
CREATE_SHARE_TYPE |
Method of specifying the shared folder |
|
EXISTSHAREFOLDERNAME |
Full path to an existing shared folder |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Port number to connect to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of port for establishing SSL connection to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address |
String value. |
SERVERCERT2048BITS |
Size of the key for the Administration Server certificate (bits) |
|
MOBILESERVERADDRESS |
Address of the Administration Server for connection of mobile devices; ignored if the MobileSupport component has not been selected |
String value. |
Network Agent installation parameters
The table below describes the MSI properties that you can configure when installing Network Agent. All of the parameters are optional, except for EULA and SERVERADDRESS.
Parameters of Network Agent installation in non-interactive mode
MSI property |
Description |
Available values |
|---|---|---|
EULA |
Acceptance of the terms of the License Agreement |
|
DONT_USE_ANSWER_FILE |
Read installation settings from response file |
|
INSTALLDIR |
Path to the Network Agent installation folder |
String value. |
SERVERADDRESS |
Administration Server address (required) |
String value. |
SERVERPORT |
Number of port for connection to Administration Server |
Numerical value. |
SERVERSSLPORT |
Number of the port for encrypted connection to Administration Server by using SSL protocol |
Numerical value. |
USESSL |
Whether to use SSL connection |
|
OPENUDPPORT |
Whether to open a UDP port |
|
UDPPORT |
UDP port number |
Numerical value. |
USEPROXY |
Whether to use a proxy server |
|
PROXYLOCATION (PROXYADDRESS:PROXYPORT)
|
Proxy address and number of port for connection to proxy server |
String value. |
PROXYLOGIN |
Account for connection to proxy server |
String value. |
PROXYPASSWORD |
Password of account for connection to proxy server (Do not specify any details of privileged accounts in the parameters of installation packages.) |
String value. |
GATEWAYMODE |
Connection gateway use mode |
|
GATEWAYADDRESS |
Connection gateway address |
String value. |
CERTSELECTION |
Method of receiving a certificate |
|
CERTFILE |
Path to the certificate file |
String value. |
VMVDI |
Enable dynamic mode for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) |
|
LAUNCHPROGRAM |
Whether to start the Network Agent service after installation |
|
NAGENTTAGS |
Tag for Network Agent (has priority over the tag given in the response file) |
String value. |
Virtual infrastructure
Kaspersky Security Center supports the use of virtual machines. You can install Network Agent and the security application on each virtual machine, and you can protect virtual machines at the hypervisor level. In the first case, you can use either a standard security application or Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Light Agent to protect your virtual machines. In the second case, you can use Kaspersky Security for Virtualization Agentless.
Kaspersky Security Center supports rollbacks of virtual machines to their previous state.
Tips on reducing the load on virtual machines
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine, you are advised to consider disabling some Kaspersky Security Center features that seem to be of little use for virtual machines.
When installing Network Agent on a virtual machine or on a template intended for generation of virtual machines, we recommend the following actions:
- If you are running a remote installation, in the properties window of the Network Agent installation package, in the Advanced section, select the Optimize settings for VDI option.
- If you are running an interactive installation through a Wizard, in the Wizard window, select the Optimize the Network Agent settings for the virtual infrastructure option.
Selecting those options alters the settings of Network Agent so that the following features remain disabled by default (before a policy is applied):
- Retrieving information about software installed
- Retrieving information about hardware
- Retrieving information about vulnerabilities detected
- Retrieving information about updates required
Usually, those features are not necessary on virtual machines because they use uniform software and virtual hardware.
Disabling the features is invertible. If any of the disabled features is required, you can enable it through the policy of Network Agent, or through the local settings of Network Agent. The local settings of Network Agent are available through the context menu of the relevant device in Administration Console.
Support of dynamic virtual machines
Kaspersky Security Center supports dynamic virtual machines. If a virtual infrastructure has been deployed on the organization's network, dynamic (temporary) virtual machines can be used in certain cases. The dynamic VMs are created under unique names based on a template that has been prepared by the administrator. The user works on a VM for a while and then, after being turned off, this virtual machine will be removed from the virtual infrastructure. If Kaspersky Security Center has been deployed on the organization's network, a virtual machine with installed Network Agent will be added to the Administration Server database. After you turn off a virtual machine, the corresponding entry must also be removed from the database of Administration Server.
To make functional the feature of automatic removal of entries on virtual machines, when installing Network Agent on a template for dynamic virtual machines, select the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option:
- For remote installation—In the properties window of the installation package of Network Agent (Advanced section)
- For interactive installation—In the Network Agent Installation Wizard
Avoid selecting the Enable dynamic mode for VDI option when installing Network Agent on physical devices.
If you want events from dynamic virtual machines to be stored on the Administration Server for a while after you remove those virtual machines, then, in the Administration Server properties window, in the Events repository section, select the Store events after devices are deleted option and specify the maximum storage term for events (in days).
Support of virtual machines copying
Copying a virtual machine with installed Network Agent or creating one from a template with installed Network Agent is identical to the deployment of Network Agents by capturing and copying a hard drive image. So, in general case, when copying virtual machines, you need to perform the same actions as when deploying Network Agent by copying a disk image.
However, the two cases described below showcase Network Agent, which detects the copying automatically. Owing to the above reasons, you do not have to perform the sophisticated operations described under "Deployment by capturing and copying the hard drive of a device":
- The Enable dynamic mode for VDI option was selected when Network Agent was installed—After each restart of the operating system, this virtual machine will be recognized as a new device, regardless of whether it has been copied or not.
- One of the following hypervisors is in use: VMware, HyperV, or Xen: Network Agent detects the copying of the virtual machine by the changed IDs of the virtual hardware.
Analysis of changes in virtual hardware is not absolutely reliable. Before applying this method widely, you must test it on a small pool of virtual machines for the version of the hypervisor currently used in your organization.
Support of file system rollback for devices with Network Agent
Kaspersky Security Center is a distributed application. Rolling back the file system to a previous state on a device with Network Agent installed will lead to data desynchronization and improper functioning of Kaspersky Security Center.
The file system (or a part of it) can be rolled back in the following cases:
- When copying an image of the hard drive.
- When restoring a state of the virtual machine by means of the virtual infrastructure.
- When restoring data from a backup copy or a recovery point.
Scenarios under which third-party software on devices with Network Agent installed affects the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder are only critical scenarios for Kaspersky Security Center. Therefore, you must always exclude this folder from the recovery procedure, if possible.
Because the workplace rules of some organizations provide for rollbacks of the file system on devices, support for the file system rollback on devices with Network Agent installed has been added to Kaspersky Security Center, starting with version 10 Maintenance Release 1 (Administration Server and Network Agents must be of version 10 Maintenance Release 1 or later). When detected, those devices are automatically reconnected to the Administration Server with full data cleansing and full synchronization.
By default, support of file system rollback detection is enabled in Kaspersky Security Center 13.1.
As much as possible, avoid rolling back the %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\KasperskyLab\adminkit\ folder on devices with Network Agent installed, because full resynchronization of data requires a large amount of resources.
A rollback of the system state is absolutely not allowed on a device with Administration Server installed. Nor is a rollback of the database used by Administration Server.
You can restore a state of Administration Server from a backup copy only with the standard klbackup utility.
Page top