Contents
- Interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications: more information
- Conventions used in interaction schemas
- Administration Server and DBMS
- Administration Server and Administration Console
- Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application
- Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
- Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
- Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
- Administration Server and two devices in DMZ: a connection gateway and a client device
- Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console
- Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
Interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and security applications: more information
This section provides the schemas for interaction of Kaspersky Security Center components and managed security applications. The schemas provide the numbers of the ports that must be available and the names of the processes that open those ports.
Conventions used in interaction schemas
The following table provides the conventions used across the schemas.
Document conventions
Icon |
Meaning |
|
Administration Server |
|
Secondary Administration Server |
|
DBMS |
|
Client device (that has Network Agent and an application from Kaspersky Endpoint Security family installed, or has a different security application installed that Kaspersky Security Center can manage) |
|
Connection gateway |
|
Distribution point |
|
Mobile client device with Kaspersky Security for Mobile |
|
Browser on the user's device |
|
Process running on the device and opening a port |
|
Port and its number |
|
TCP traffic (the arrow direction shows the traffic flow direction) |
|
UDP traffic (the arrow direction shows the traffic flow direction) |
|
COM invoke |
|
DBMS transport |
|
DMZ boundary |
Administration Server and DBMS
Data from the Administration Server enter the SQL Server, MySQL, or MariaDB database.
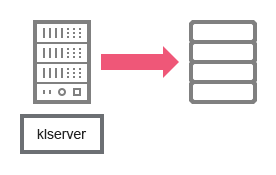
Administration Server and DBMS
If you install the Administration Server and the database on different devices, you must make available the necessary ports on the device where the database is located (for example, port 3306 for MySQL Server and MariaDB Server, or port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server). Please refer to the DBMS documentation for the relevant information.
Administration Server and Administration Console
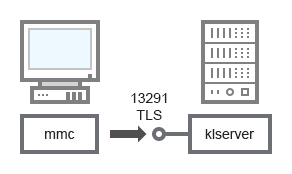
Administration Server and Administration Console
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server and Administration Console (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13291 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Administration Console |
Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application
The Administration Server receives connection from Network Agents via SSL port 13000 (see figure below).
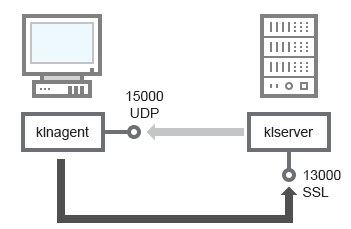
Administration Server and client device: managing the security application, connection via port 13000 (recommended)
If you used an earlier version of Kaspersky Security Center, the Administration Server on your network can receive connections from Network Agents via non-SSL port 14000 (see figure below). Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 also supports connection of Network Agents via port 14000, although using SSL port 13000 is recommended.
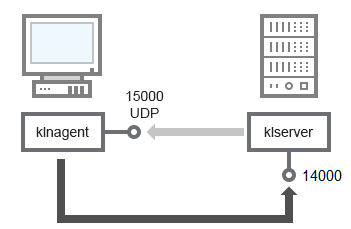
Administration Server and client device: managing the security application, connection via port 14000 (lower security)
For clarifications of schemas, see the table below.
Administration Server and client device: Managing the security application (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS (for TCP only) |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
15000 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Null |
Multicasting for Network Agents |
Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server |
14000 |
klserver |
TCP |
No |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
The client device connects to the distribution point via port 13000 and, if you are using the distribution point as a push server, also via port 13295; the distribution point multicasts to Network Agents via port 15000 (see figure below).
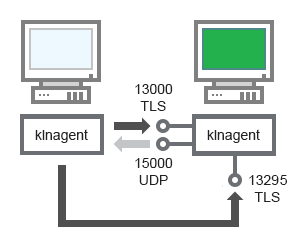
Upgrading software on a client device through a distribution point
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Upgrading software through a distribution point (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS (for TCP only) |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
15000 |
klnagent |
UDP |
Null |
Multicasting for Network Agents |
Distribution point |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Distribution point |
13295 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Sending push notifications to Network Agent |
Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
The schema (see figure below) shows how to use port 13000 to ensure interaction between Administration Servers combined into a hierarchy.
When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Administration Console connects to the Administration Server through port 13291.
Subsequently, when the Administration Servers are combined into a hierarchy, you will be able to administer both of them by using Administration Console connected to the primary Administration Server. Therefore, the accessibility of port 13291 of the primary Administration Server is the only prerequisite.
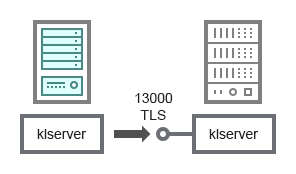
Hierarchy of Administration Servers: primary Administration Server and secondary Administration Server
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Primary Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from secondary Administration Servers |
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
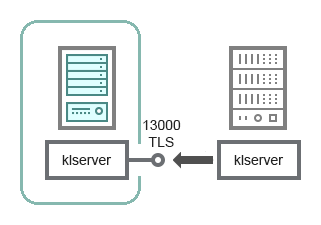
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ
The schema shows a hierarchy of Administration Servers in which the secondary Administration Server located in DMZ receives a connection from the primary Administration Server (see the table below for schema clarifications). When combining two Administration Servers into a hierarchy, make sure that port 13291 is accessible on both Administration Servers. Administration Console connects to the Administration Server through port 13291.
Subsequently, when the Administration Servers are combined into a hierarchy, you will be able to administer both of them by using Administration Console connected to the primary Administration Server. Therefore, the accessibility of port 13291 of the primary Administration Server is the only prerequisite.
Hierarchy of Administration Servers with a secondary Administration Server in DMZ (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Secondary Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from the primary Administration Server |
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
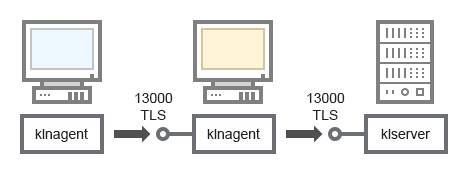
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server, a connection gateway in a network segment, and a client device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13000 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Network Agent |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server and two devices in DMZ: a connection gateway and a client device
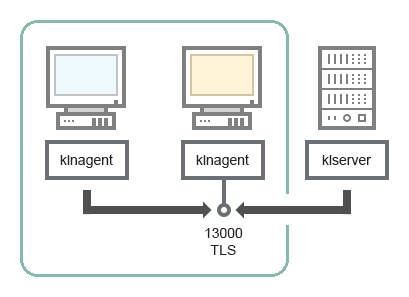
Administration Server with a connection gateway and a client device in DMZ
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server with a connection gateway in a network segment and a client device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Network Agent |
13000 |
klnagent |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Network Agents |
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console
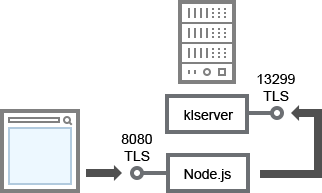
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Administration Server and Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13299 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console to the Administration Server over OpenAPI |
Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console Server or Administration Server |
8080 |
Node.js: Server-side JavaScript |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console |
Kaspersky Security Center 13.1 Web Console can be installed on the Administration Server or on another device.
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
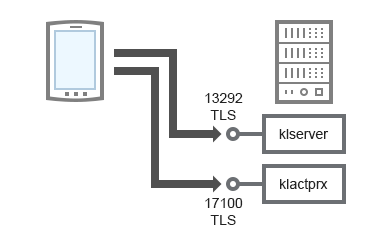
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device
For schema clarifications, see the table below.
Activating and managing the security application on a mobile device (traffic)
Device |
Port number |
Name of the process that opens the port |
Protocol |
TLS |
Port purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Administration Server |
13292 |
klserver |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections from Administration Console to Administration Server |
Administration Server |
17100 |
klactprx |
TCP |
Yes |
Receiving connections for application activation from mobile devices |














